Figure 11. Scheme illustrating bivalent regulation of cAMP synthesis by G proteins.
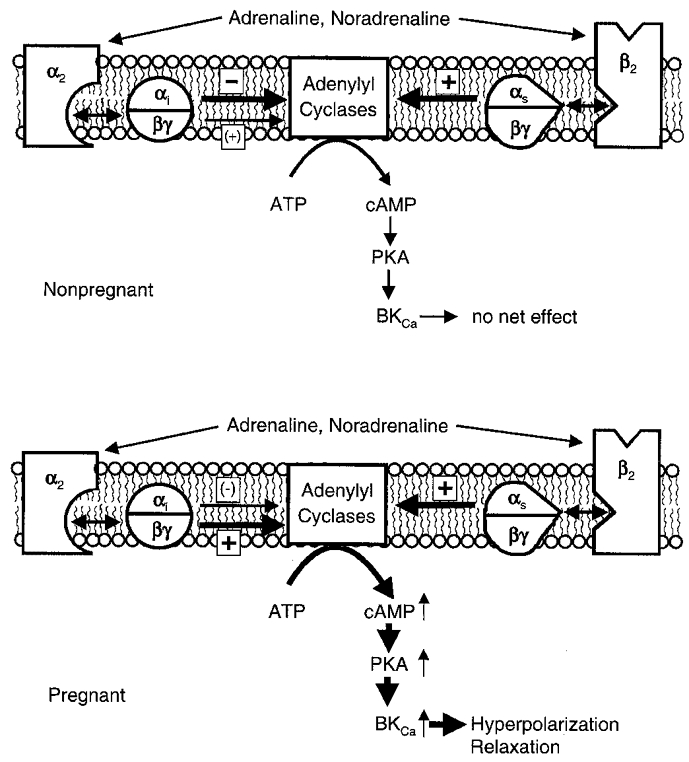
Shown is the α2- and β-AR coupling to AC in cells of the non-pregnant (upper panel) and pregnant myometrium (lower panel). Catecholamines are the physiological AR ligands which act simultaneously through receptors coupled to stimulatory (s) and inhibitory (i) G proteins. The thickness and position of arrows between G protein subunits and AC indicate the predominant effect and the subunit involved in the respective signal transduction pathway. Note that the G proteins must bind GTP and dissociate before they become active.
