Figure 7. mEPSCs support a postsynaptic mechanism for PPD at high release probabilities.
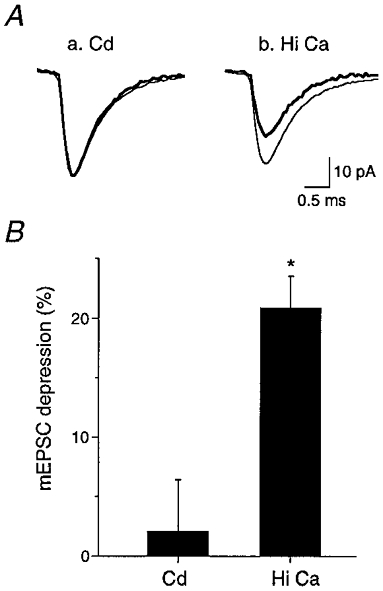
A, control AMPA mEPSCs were collected in a time period prior to paired-pulse stimulation (thin trace) and test mEPSCs were collected 30 ms following paired-pulse stimulation (thick trace). The comparison of control mEPSCs versus test mEPSCs was performed at both low (a, Cd; 4 or 8 μM) and high Pr (b, Hi Ca; 4 mM). A difference was observed under elevated calcium conditions (b). B, the test mEPSCs were not significantly depressed compared to control at low Pr in the presence of cadmium (Cd; n = 7). However, at high Pr (Hi Ca), the test mEPSCs were significantly depressed by 20.9 ± 2.7 % (n = 5; * P < 0.01).
