Figure 2. Effect of co-application of caffeine and ryanodine on spontaneous action potentials in the guinea-pig urinary bladder.
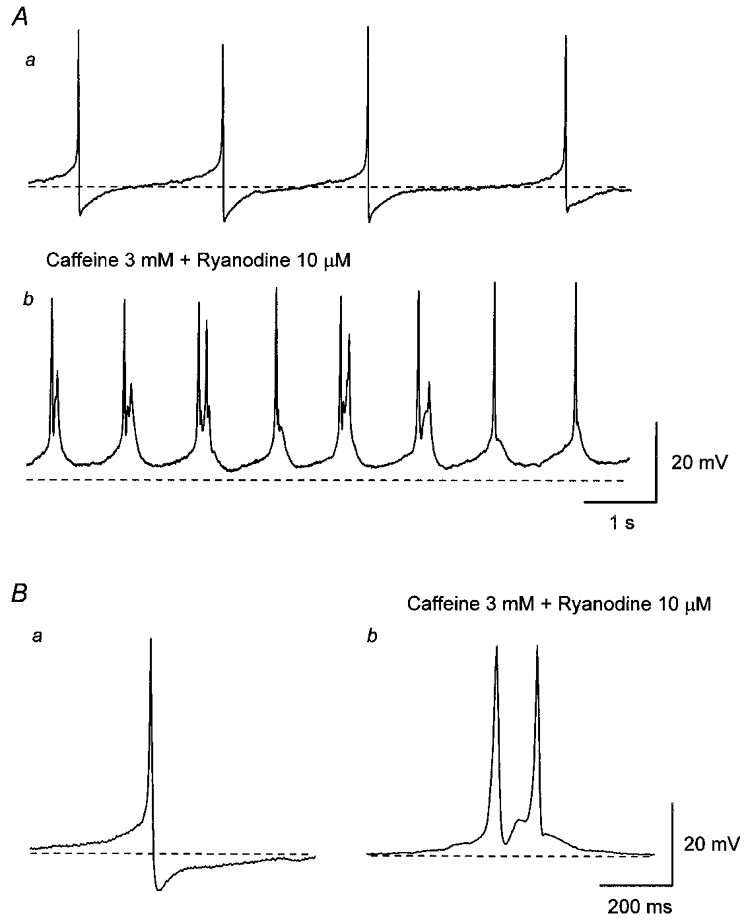
Aa, in control solution, bladder smooth muscle cells discharged spontaneous action potentials. b, co-application of caffeine (3 mM) and ryanodine (10 μM) depolarised the membrane and increased the frequency of spontaneous action potentials. Ba, in control solution, each action potential consisted of an initial slow depolarising phase and subsequent regenerative depolarisation which was followed by a rapid repolarising phase with an after-hyperpolarisation. b, in the presence of caffeine and ryanodine, each action potential had a similar amplitude and rising phase to those of control action potentials but had a longer duration. It also can be seen that action potentials lacked an after-hyperpolarisation and often multiple action potentials were discharged (Ab and Bb). All traces were recorded from the same cell. Scale bar on the right in A refers to both traces in A. Scale bar on the right in B refers to both traces in B. Resting membrane potential was -43 mV.
