Figure 9. Effects of low chloride solution and niflumic acid on EJPs and contractions recorded from the sac of the rat penile bulb.
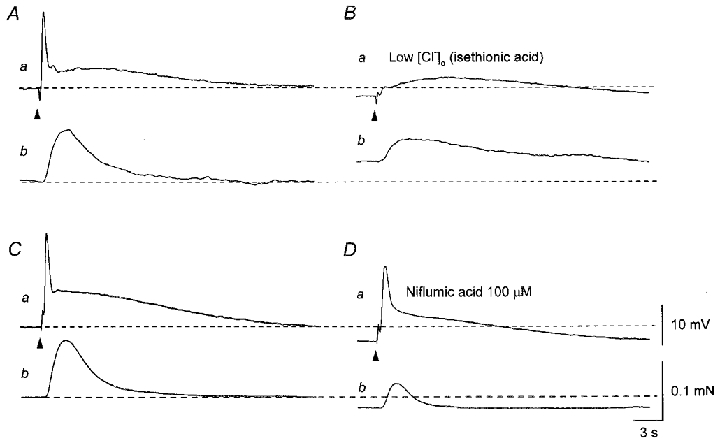
In the presence of nifedipine (10 μM), three impulses delivered at 20 Hz initiated an EJP which consisted of two components and an associated contraction (Aa and b). Low chloride solution hyperpolarised the membrane and selectively inhibited the amplitude of the rapid component of the EJP without inhibiting the slow component (Ba). Low chloride solution caused a contraction and also inhibited the nerve-evoked contraction (Bb). In a different preparation exposed to nifedipine, three impulses delivered at 20 Hz initiated an EJP which consisted of two components and an associated contraction (Ca and b). Niflumic acid (100 μM) hyperpolarised the membrane and reduced the amplitude of the EJP (Da). Niflumic acid (100 μM) caused relaxation and also inhibited the nerve-evoked contraction (Db). A and B, and C and D were recorded from two different cells. Resting membrane potentials were -47 mV in A and B and -54 mV in C and D. Scale bars in D refer to corresponding traces in A–C.
