Figure 1. Anatomical compartments of the thigh and quantification of the knee-extensor muscle mass.
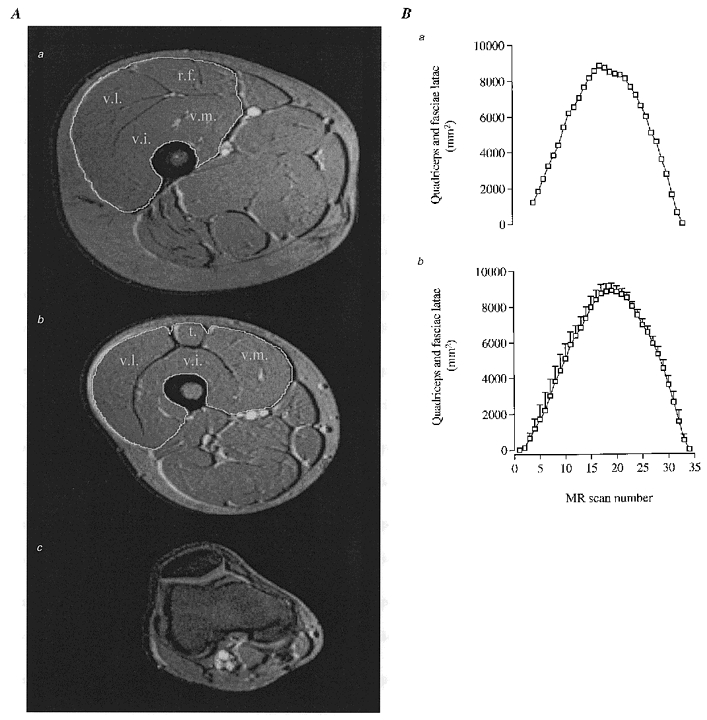
A, MRI of cross-sections of upper-thigh (a) and mid-thigh (b) with the white line indicating borders of quadriceps femoris muscle, including vastus lateralis (v.l.), vastus intermedius (v.i.), vastus medialis (v.m.), rectus femoris (r.f.) and tendon of quadriceps femoris muscle (t). A cross-section of the distal end is shown in c. It was sometimes difficult to exactly determine the origin of the muscles at the proximal end (a). This was solved by plotting the serial individual cross-sections and determining the origin by extrapolation (see Ba). Mean values ±s.e.m. for all subjects’ serial cross-sections of the thigh are shown in Bb.
