Figure 3. The respiratory and cardiovascular effects of distension of the urinary bladder in the spontaneously breathing animal.
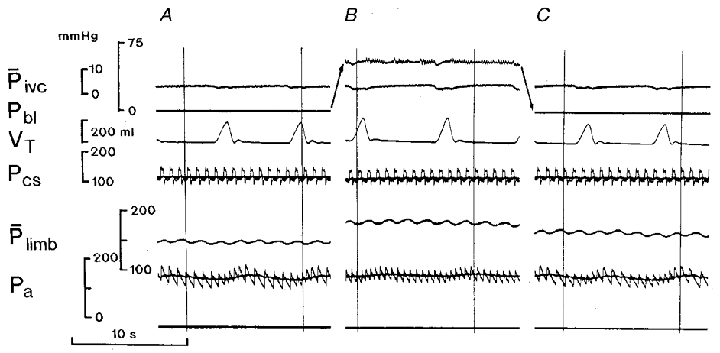
Arterialized blood perfusion of the vascularly isolated carotid bifurcation regions. Carotid sinus pressures (phasic and mean) were maintained constant. A and C, control records taken at zero urinary bladder pressure. B, distension of the bladder. Records from top to bottom: Pivc, inferior vena caval mean pressure; Pbl, urinary bladder pressure; VT, tidal volume (inspiration upwards); Pcs, phasic and mean carotid sinus perfusion pressure; Plimb, hindlimb mean perfusion pressure; Pa, phasic and mean arterial blood pressure. Note: the arrows are used for clarity and indicate the movements of the record for bladder pressure, from A to B and from B to C.
