Figure 2. Electrical properties of interstitial and smooth muscle cells.
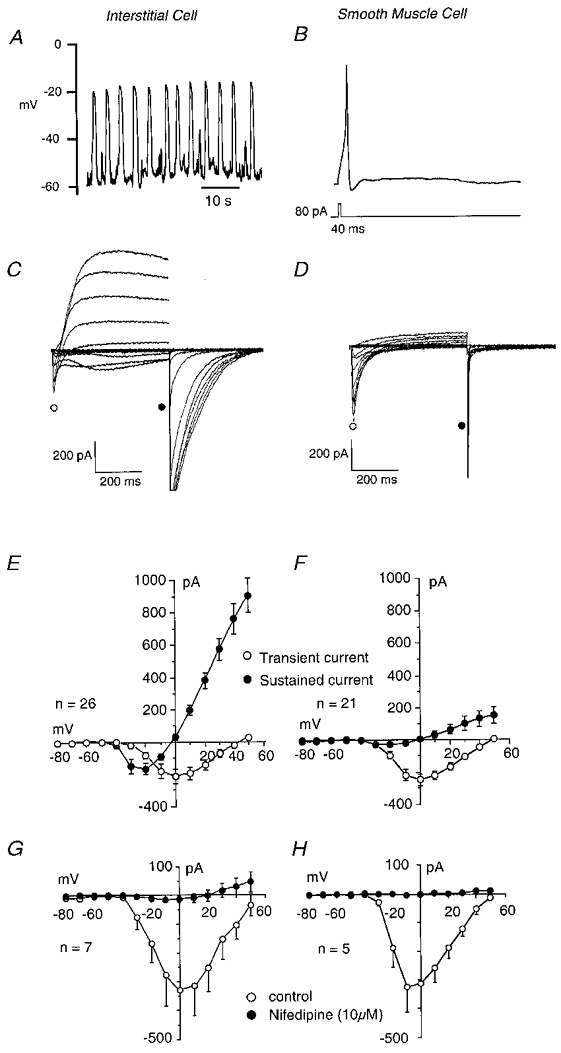
Interstitial cells showed regular ‘slow-wave’ depolarisations in current clamp (A) while smooth muscle cells were usually quiescent, although they could produce an action potential in response to depolarising current (B). Under voltage clamp, interstitial cells exhibited both L-type calcium currents and calcium-activated chloride currents (C) while the smooth muscle cells showed predominantly L-type calcium currents (D). E and F show summaries of the currents measured in 26 interstitial and 21 smooth muscle cells. Nifedipine (10 μm) blocked ICa both in interstitial (G) and in smooth muscle cells (H).
