Figure 4. Spontaneous activity in interstitial cells.
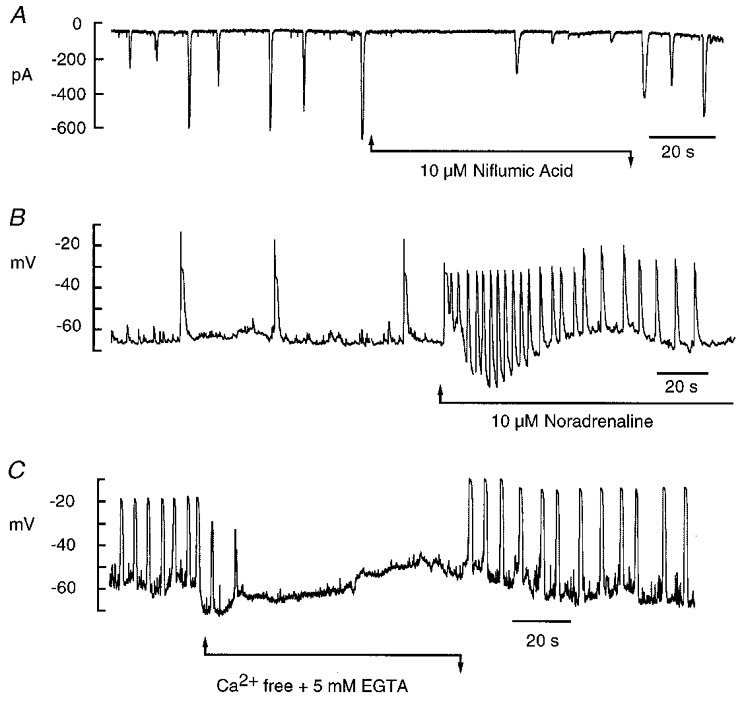
A, in voltage-clamp mode interstitial cells typically showed spontaneous transient inward currents which could be reduced in both amplitude and frequency by 10 μm niflumic acid. B, in current-clamp mode the interstitial cells fired spontaneous depolarisations at a frequency of about 1.5 min−1 and this was increased to 18 min−1 in the presence of 10 μm noradrenaline. C, when the interstitial cells were perfused with Ca2+-free Hanks’ solution containing 5 mm EGTA, spontaneous depolarisations were abolished.
