Figure 6. Kinetics, [Ca2+]o dependence and ion permeation properties of IHA and IDA.
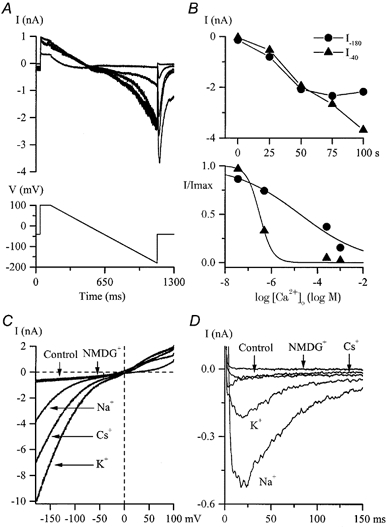
A, typical currents during a slow voltage ramp from +100 to −180 mV and a voltage step to −40 mV slowly developing after Ca2+ and Mg2+ removal from the external solution. Superimposed current traces were recorded at 25 s intervals. B, top, maximal amplitudes of inward currents at −180 mV (•, IHA) and at −40 mV after the ramp (8, IDA) plotted against time where time zero represents the moment of Ca2+ and Mg2+ removal from the external solution. Bottom, dependence of IHA (•) and IDA (8) in the same cell on the external free Ca2+ concentration. Relative currents were fitted by logistic functions with IC50 values of 20 μm for IHA and 311 nm for IDA. C and D, external cation substitution experiments were performed on two different cells after IHA(C) and IDA(D) had been stabilized in a divalent cation-free external solution. The control I-V relationship for IHA (voltage protocol as in A) and control current response for IDA (voltage step from −100 to −40 mV) were obtained in high-Na+, 2.5 mm CaCl2-containing external solution. Traces labelled ‘Na+’ were obtained after Ca2+ removal whereas all other traces were obtained in solutions with Na+ replacement as described in the Methods. High-Cs+ pipette solution was used.
