Figure 1. Age-associated increases in muscle sympathetic nerve activity.
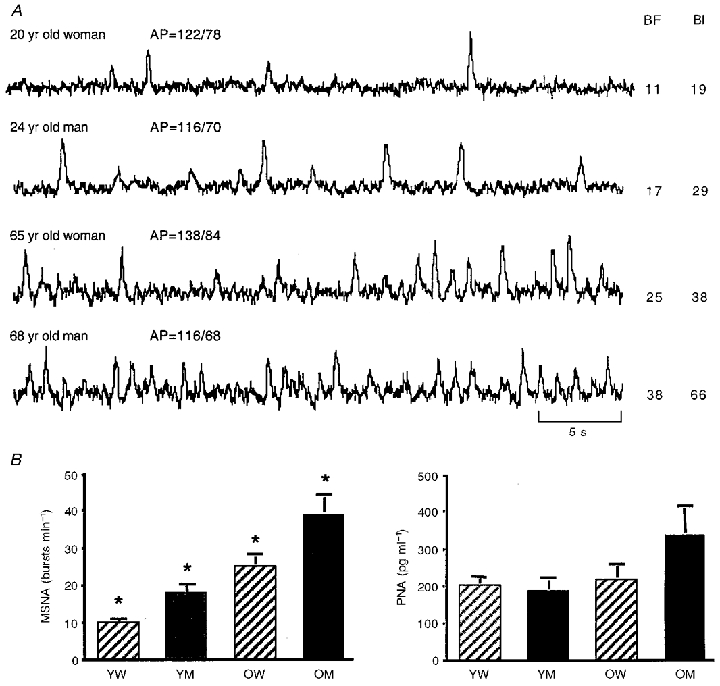
A, integrated peroneal neurograms of muscle sympathetic nerve activity (MSNA) from 4 healthy adult humans under supine resting conditions (top to bottom): young female, young male, older female, older male. MSNA burst frequency (BF; bursts min−1) and burst incidence (BI; bursts (100 heart beats)−1) are higher in the neurograms of the older adults in both sexes. However, the female subjects demonstrate lower MSNA than the males at each age. AP, arterial blood pressure. B, mean ±s.e.m. values for peroneal MSNA in 4 groups of subjects: young women (YW), young men (YM), older women (OW) and older men (OM). MSNA was at least twice as great in the older compared with the young subjects of the same sex. At each age, however, MSNA was significantly lower in the women. These age and sex differences in MSNA were not reflected in the corresponding antecubital venous plasma noradrenaline concentrations. PNA, plasma noradrenaline concentration; *P < 0·05 vs. all other groups.
