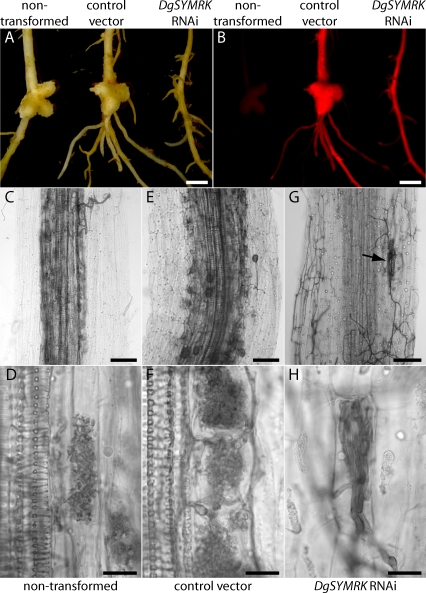
Figure 2. Nodulation and AM Formation Are Impaired in DgSYMRK Knockdown Roots.
Co-transformed roots express DsRED1 as visible marker.
(A and B) Nodulated wild-type root (left), control root transformed with pRedRoot lacking the silencing cassette (middle), and non-nodulated DgRNAi knockdown root (right) (A) under white light and (B) with transgenic roots showing DsRED1 fluorescence.
(C–H) AM phenotype of D. glomerata (Datisca) wild type, transgenic control, and DgSYMRK knockdown roots. (C and D) Wild-type and (E and F) transgenic control roots are well colonized and show arbuscules in inner cortical cells. (G and H) Typical DgSYMRK knockdown root with no AM formation but extraradical mycelium and aborted fungal infections (H and arrow in G). Such features were not seen in Datisca wild-type or transgenic control roots and are reminiscent of those observed on L. japonicus symrk mutant roots (Figure 3). Roots were inoculated simultaneously with Frankia bacteria and G. intraradices (8 wk). Transgenic and regenerated nontransgenic roots of 27 (control) and 23 (DgSYMRK RNAi construct) plants from three independent experiments were tested. Independent transformed roots examined were n = 42 (control) and n = 55 (DgSYMRK RNAi).
Scale bars: (A and B) 2 mm; (C, E, and G) 0.1 mm; (D, F, and H) 0.02 mm.