Figure 3. Abnormal fusion of the lower incisors.
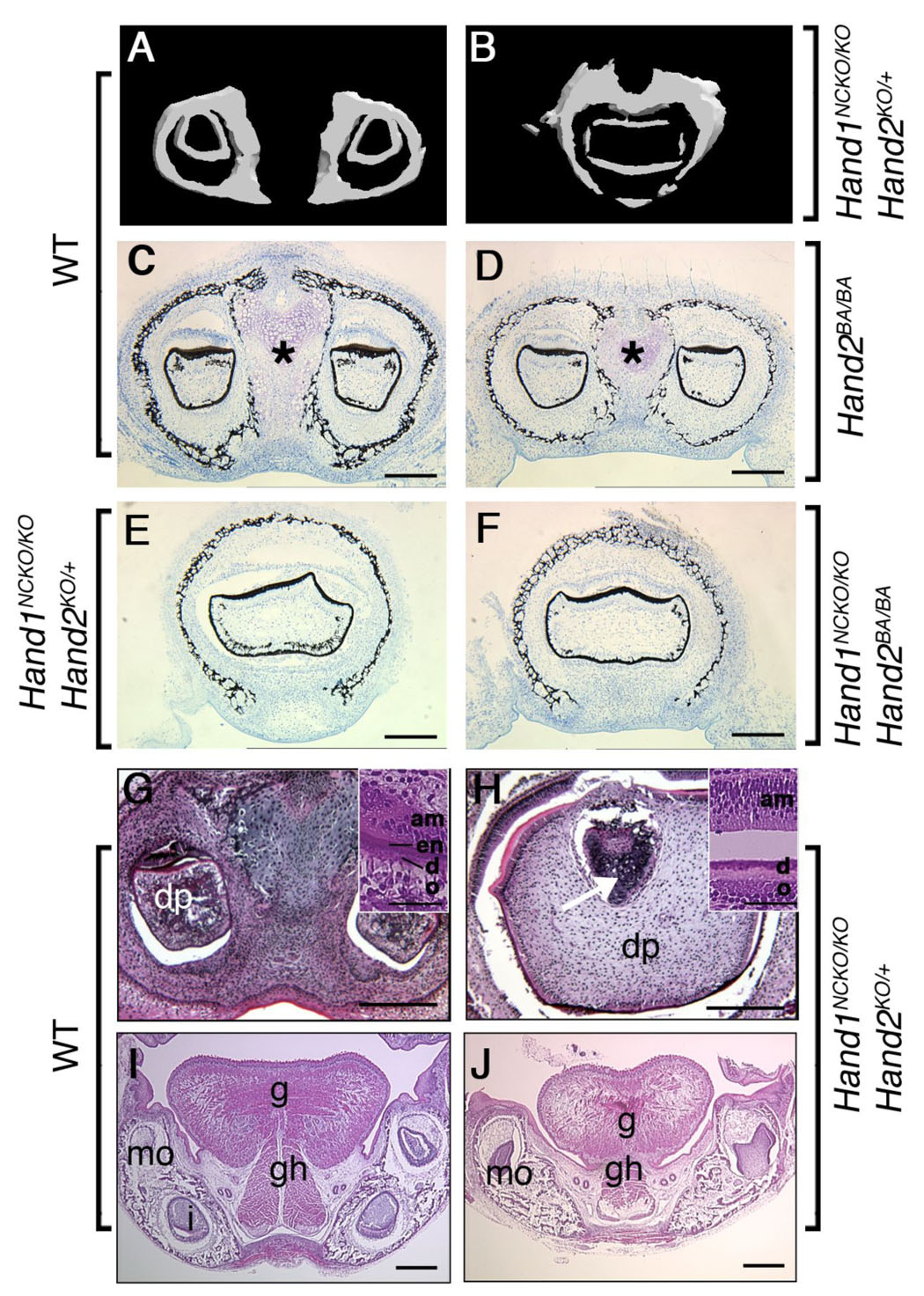
(A, B) Micro-CT analysis of the lower incisors in P1 embryos. In wild-type embryo (A), two lower incisors are located within the mandible. In contrast, a large deformed single incisor is observed within the fused mandible of the mutant (B). (C–F) Von Kossa staining of coronal sections of the mandible in plastic-embedded wild-type (C), Hand2BA/BA (D), Hand1NCKO/KO;Hand2KO/+ (E) and Hand1NCKO/KO;Hand2BA/BA (F) embryos. In wild-type embryos, a well-developed distal symphysis of Meckel’s cartilage is observed (asterisk in C). The symphysis is much smaller in the Hand2BA/BA mutant (asterisk in D) and becomes undetectable in Hand1NCKO/KO;Hand2KO/+ and Hand1NCKO/KO;Hand2BA/BA embryos (E, F). Fused incisors are seen in mutant embryos (E, F). (G–J) H&E staining of coronal paraffin sections of P1 wild-type (G, I) and Hand1NCKO/KO;Hand2KO/+ (H, J) embryos. (G, H) In wild-type embryos (G), two incisors with normal cytodifferentiation, including dental papilla (dp), odontoblasts (o), dentin (d), enamel (en) and ameloblasts (am) are observed (inset in G). In the mutant (H), a large fused incisor is observed, and the enamel layer is absent (inset in H). The distal symphysis is embedded in the dental papilla (H, arrow). (I, J) Well-developed extrinsic muscles (g; genioglossus, gh; geniohyoid) are observed in the tongue of wild-type embryos (I). In the mutant (J), muscle fibers are sparse and hypoplastic. Bars indicate 100 µm (C–J) and 40 µm (inset in G and H). mo; molar, i; incisor.
