Figure 3.
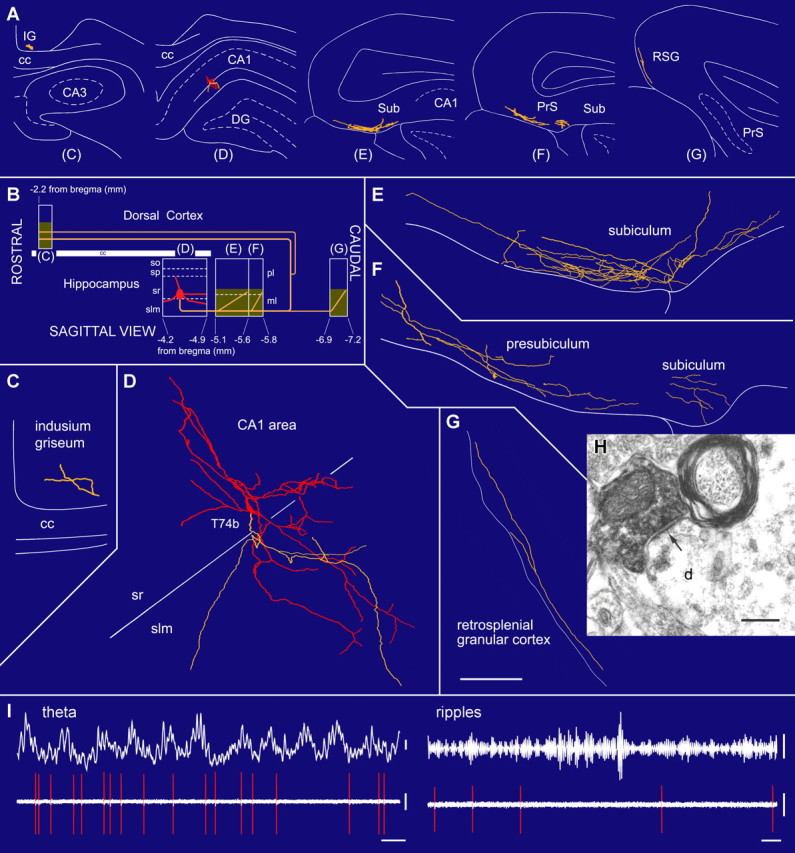
A radiatum-retrohippocampal projection neuron (T74b) recorded in vivo in the dorsal CA1 area innervating the subiculum (Sub), presubiculum (PrS), retrosplenial cortex (RSG), and indusium griseum (IG). A, The soma (red), dendrites (red), and axons (yellow) in coronal planes from selected sections as indicated in B. B, Representation in the sagittal plane showing the rostrocaudal extent of the dendrites and axon. The soma is located at the border of str. radiatum and lacunosum-moleculare. The axon, traced over 5 mm, runs toward caudal regions through the subiculum and presubiculum and then bifurcates into additional caudal and rostral branches. Shaded areas represent the distribution of boutons in the reconstructed sections. C–G, Soma and dendrites are shown complete; the axon is shown from selected sections (blocks in B), with very few local collaterals within the hippocampus. The long-range axon innervates the molecular layer in the subiculum and other caudal areas such as the retrosplenial granular cortex. H, Electron micrograph of a neurobiotin-filled bouton making a type II synapse (arrow) with a dendritic shaft that also receives a type I synapse in the subiculum. I, In vivo firing patterns show that the cell fires at the descending phase of extracellular theta oscillations (filter, direct current-220 Hz) recorded from a second electrode in the pyramidal layer. During ripple episodes (top right, 90–140 Hz bandpass), the cell did not increase its firing. cc, Corpus callosum; slm, str. lacunosum-moleculare; so, str. oriens; sp, str. pyramidale; sr, str. radiatum. Scale bars: (in G) C–G, 100 μm; H, 0.2 μm. Calibration: I, theta, 0.2 mV; ripples, 0.05 mV, 0.1 s; spikes, 0.5 mV.
