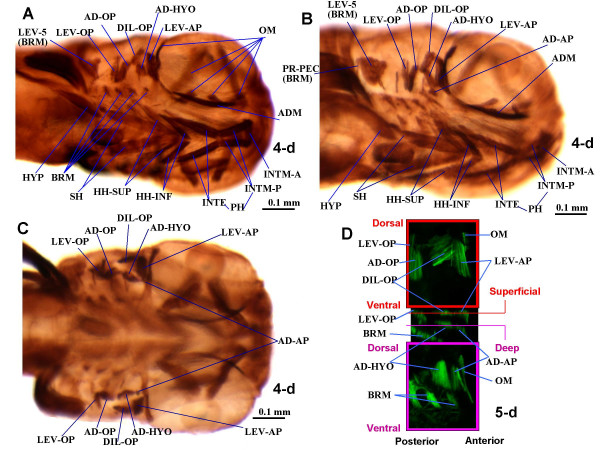
Figure 2.
Larval musculature of the zebrafish head. Ventrolateral (A, B, showing different angles and certain distinct structures) and dorsal (C) views of immunohistochemical detection of myosin heavy chain in the cephalic muscles of 4-d zebrafish larvae (3.0 mm TL). Anterior to right. D. Confocal images showing green fluorescent protein (GFP) in the muscles adductor arcus palatini, adductor hyomandibulae, dilatator operculi and levator arcus palatini of a 5-d transgenic zebrafish larva expressing a GFP reporter driven from the muscle-specific alpha-actin promoter. Upper and lower panels: XY confocal optical sections through superficial and deep musculature, respectively. Central panel: XZ confocal reconstruction showing the plains of the confocal XY sections. AD-AP, adductor arcus palatini; AD-HYO, adductor hyomandibulae; AD-OP, adductor operculi; ADM, adductor mandibulae; BRM, branchial muscles; DIL-OP, dilatator operculi; HH-INF, hyoideus inferior; HH-SUP, hyoideus superior; HYP, hypaxialis; INTE, interhyoideus; INTM-A, INTM-P, intermandibularis anterior and posterior; LEV-AP, levator arcus palatini; LEV-OP, levator operculi; LEV-5, levator arcus branchialis 5; OM, ocular muscles; PR-H, protractor hyoideus; PR-PEC, protractor pectoralis; SH, sternohyoideus.