Fig. 1.
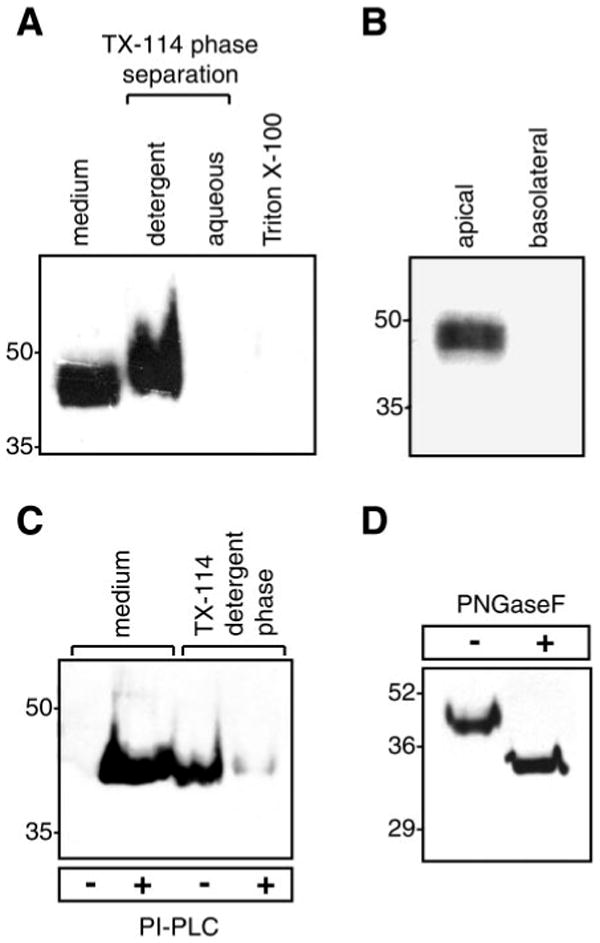
Endogenous expression and posttranslational modifications of prostasin in M-1 kidney epithelial cells. A: immunoblot of native prostasin. Proteins were extracted from M-1 cells in 1% Triton X-100 or by detergent phase separation using 2% Triton X-114 (TX-114). Samples were normalized for cell number and separated by SDS-PAGE. B: immunoblot for prostasin in apical and basolateral conditioned media from M-1 cells grown to confluence [transepithelial resistance (Rte) > 1,000 Ω × cm2] on 0.4-μm-pore filters. C: glycosylphosphatidylinositol (GPI) anchoring of prostasin. M-1 cells were treated with phosphatidylinositol-specific phospholipase C (PI-PLC) or PBS. Prostasin was assayed in conditioned medium and detergent phase cell lysates by immunoblotting. D: deglycosylation of prostasin. M-1 cells were treated with PI-PLC, concentrated conditioned medium was incubated with protein N-glycosidase F (PNGase F), and proteins were separated by SDS-PAGE and immunoblotted to detect prostasin.
