Fig. 2.
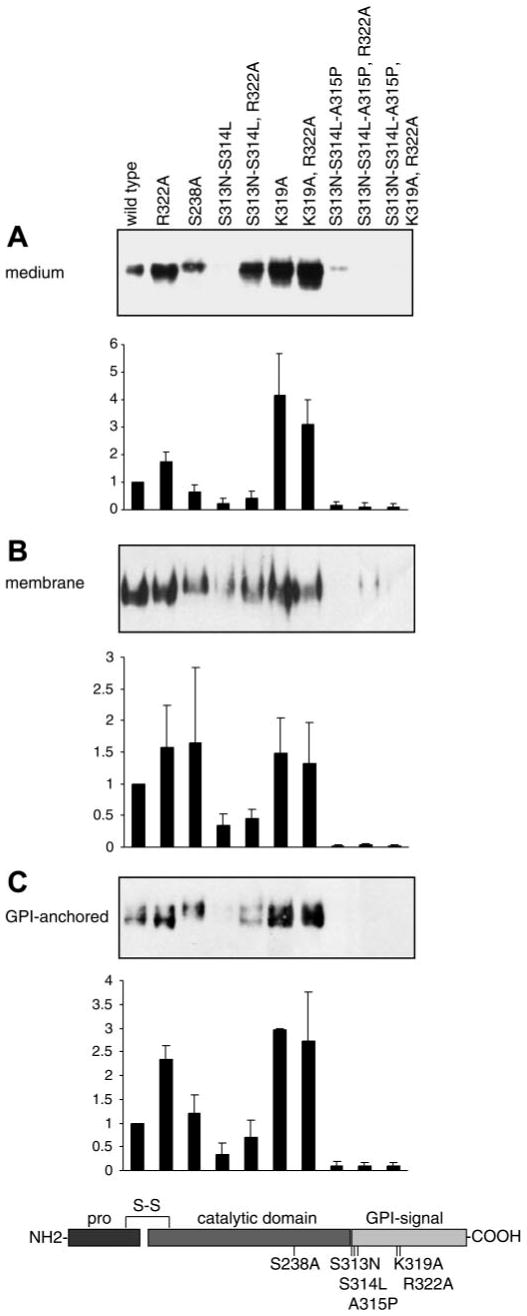
Determinants of secretion and GPI anchoring of mouse prostasin in M-1 cells. Specific amino acid mutations were introduced into prostasin to disrupt residues hypothesized to regulate GPI anchoring and secretion of prostasin as shown in the schematic diagram. Samples from M-1 cells transiently transfected with prostasin mutants were analyzed by immunoblotting and densitometry. A: conditioned medium was concentrated and normalized to load equivalent volumes; results were identical when loading was normalized to cell number. B: proteins were extracted from transfected M-1 cells by Triton X-114 detergent phase separation, precipitated with 15% trichloroacetic acid (TCA), and normalized to cell number for analysis. C: transiently transfected M-1 cells were treated with PI-PLC to release cell surface GPI-anchored proteins. Conditioned medium was concentrated, and gel loading was normalized to cell number. All experiments were done at least 3 times, and representative blots are shown. Prostasin in each compartment was quantified by densitometry and data is expressed as ratio of prostasin mutation to wild-type densitometric units. Data are expressed as means ± SD (n = 3–7).
