Fig. 4.
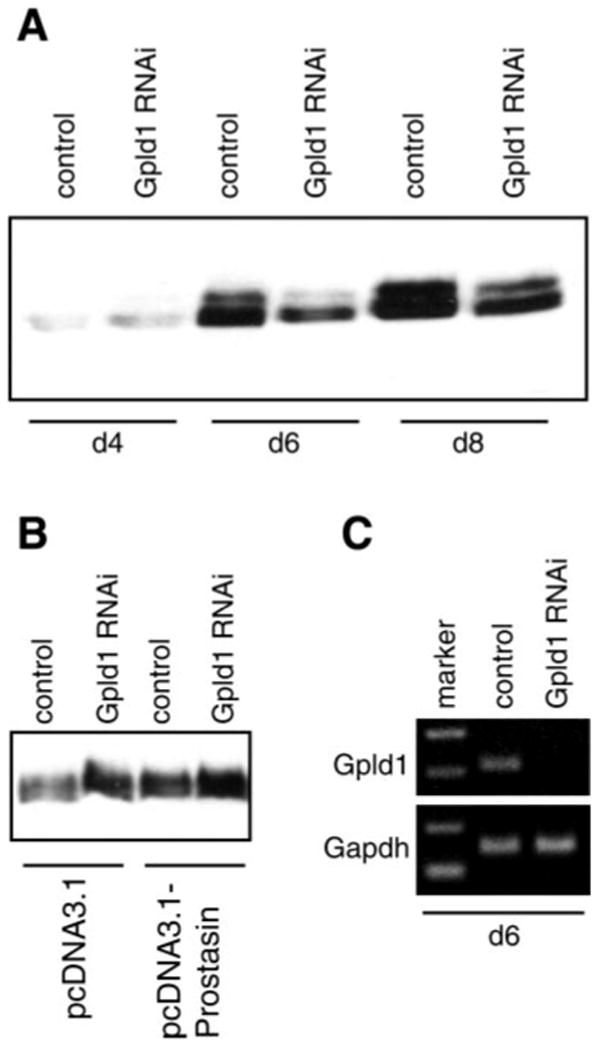
GPI-specific phospholipase D (Gpld1)-dependent secretion of prostasin. M-1 cells were transfected with Gpld1-specific small interfering RNA (siRNA) or control siRNA. A: conditioned medium was collected at 48-h intervals, concentrated, normalized to cell number, and assayed for prostasin by immunoblotting. There was no difference in cell proliferation between Gpld1- and control siRNA-transfected cells (data not shown). Relative levels of prostasin in conditioned medium were quantified by densitometry and expressed as means ± SD. Transfection with Gpld1 siRNA reduced prostasin in conditioned medium by 74% (P < 0.05; n = 3). B: M-1 cells stably transfected to express prostasin or empty vector (see Experimental Procedures and Fig. 5 for details) were transfected with Gpld1 or control siRNA and treated with PI-PLC. Medium was assayed for prostasin by immunoblotting. Inhibition of Gpld1 increased PI-PLC-releasable prostasin. C: expression of Gpld1 was assessed by semiquantitative RT-PCR relative to glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase (GAPDH) control 6 days after transfection with Gpld1 and control siRNA. d4, d6, d8, 4, 6, and 8 days after transfection.
