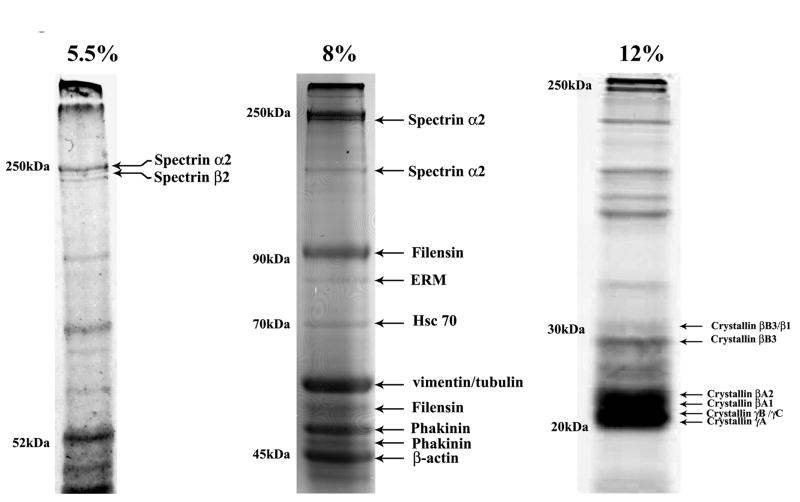
Figure 1.
SDS-polyacrylamide gel electrophoretic separation and MALDI-TOF-TOF mass spectrometry-based identification of proteins in the triton insoluble fractions of mouse lens fibers.
To identify the major proteins of the lens fiber cell triton insoluble fraction, tissues were processed as described in Methods and separated by SDS-PAGE, using gels containing 5.5, 8 and 12% acrylamide. Gels were stained with GelCode blue and distinctly separated protein bands excised, subjected to in-gel tryptic digestion and MALDI-TOF-TOF MS analysis. Representative photographs of the GelCode stained SDS-PAGE gels are shown. The MALDI-TOF-TOF based protein identity is indicated next to the corresponding protein band on the gels.