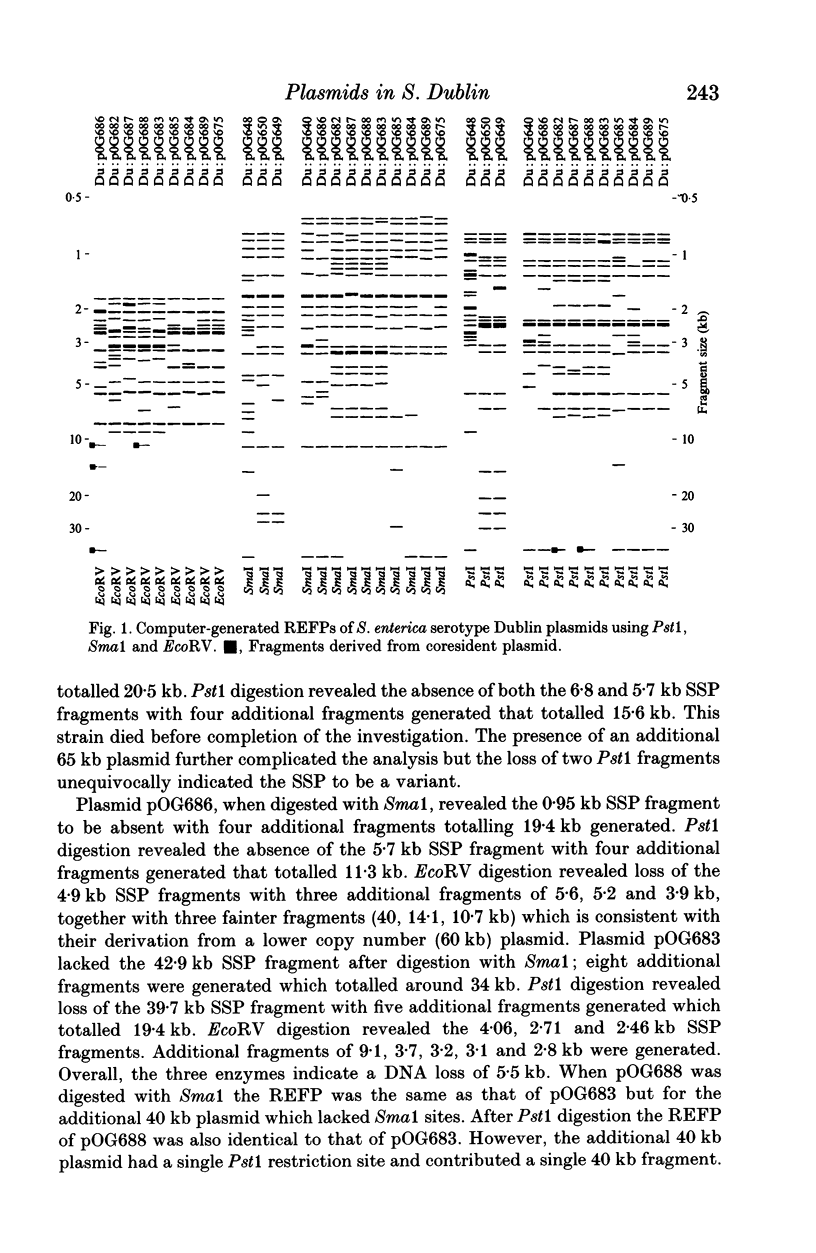
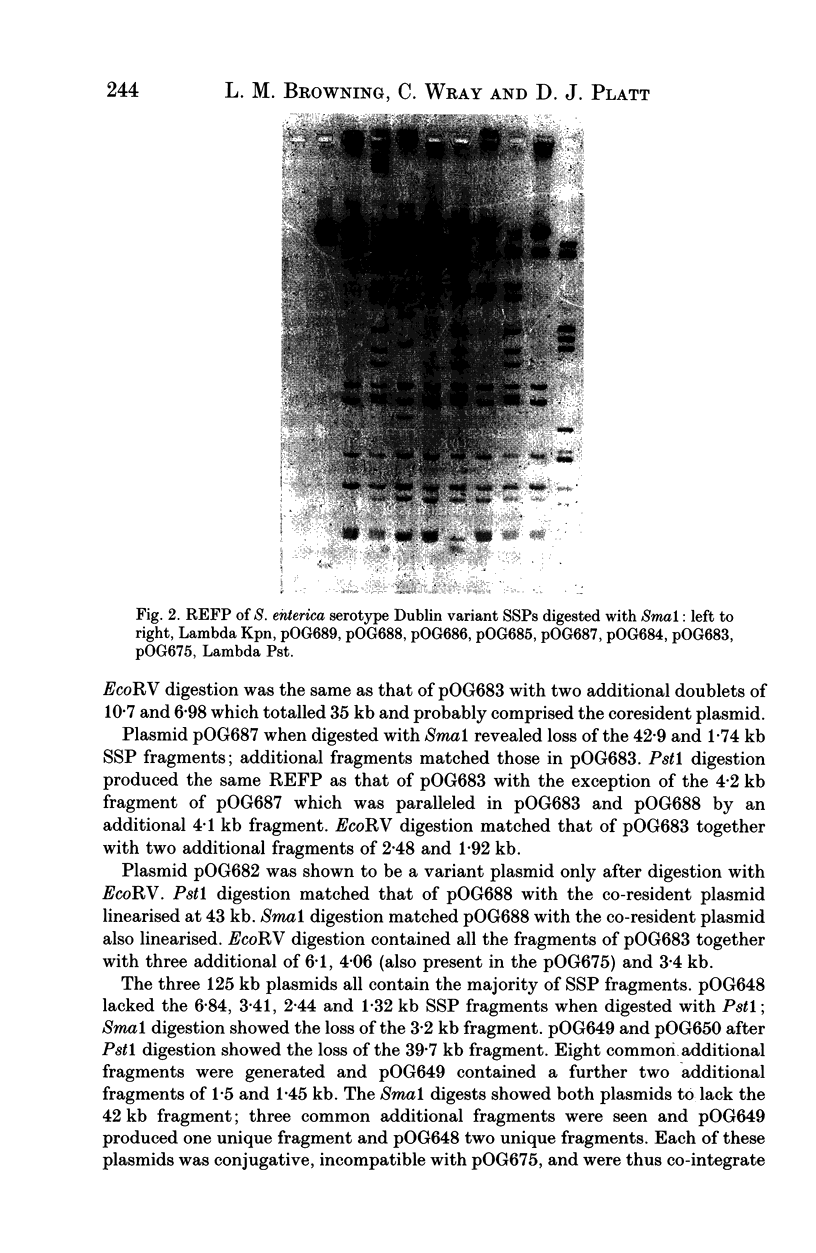
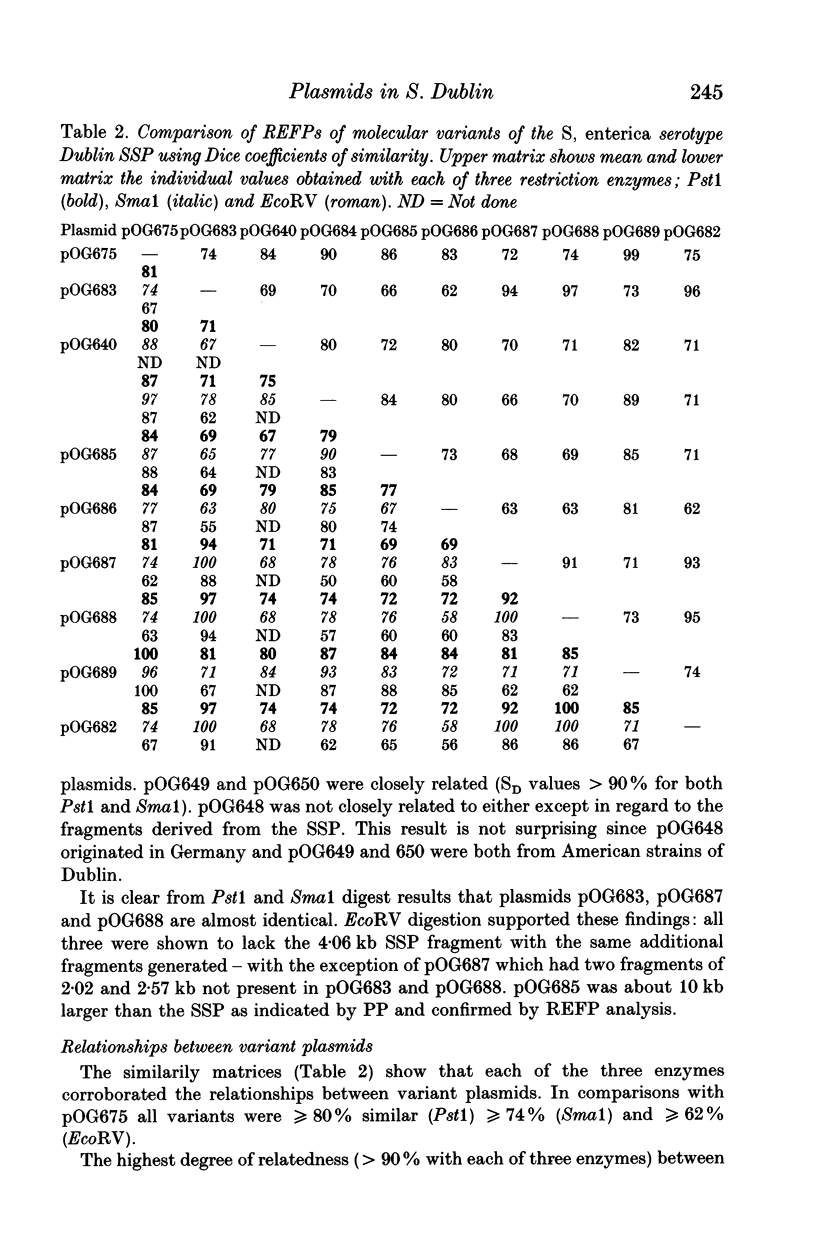
Abstract
Molecular variation within and between plasmids of Salmonella enterica serotype Dublin was analysed. Such variation has been demonstrated in the serotype-specific plasmids (SSP's) of Typhimurium and Enteritidis. The two aims of this study were to determine the plasmid diversity in a host-adapted serotype and also the incidence of molecular variation in the SSP among strains of Dublin using restriction endonuclease fragmentation pattern (REFP) analysis with Pst1, Sma1 and EcoRV. Sixty-five strains were examined from seven countries. Plasmid profile and REFP analysis showed that none of the strains was plasmid-free. Seventy-seven percent of the strains possessed the 72 kb SSP either alone or in combination with another plasmid; 23% harboured plasmids which were molecular variants of the SSP. Four of the variants were more closely related to each other than to the reference SSP and were harboured by Dublin isolated from both the USA and Europe. A further three were shown to be cointegrate plasmids and were similarly distributed. Thirty-two percent of strains possessed the SSP alone. None of the UK strains was resistant to any of the antimicrobial agents tested whereas 74% of the remaining strains were resistant to between one and five antimicrobial agents. This study corroborates previous findings concerning the high degree of stability of the SSP and confirmed the clonal nature of Dublin. Co-resident plasmids provided evidence of sub-clones within localized geographical areas.
Full text
PDF








Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baird G. D., Manning E. J., Jones P. W. Evidence for related virulence sequences in plasmids of Salmonella dublin and Salmonella typhimurium. J Gen Microbiol. 1985 Jul;131(7):1815–1823. doi: 10.1099/00221287-131-7-1815. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barrow P. A., Lovell M. A. The association between a large molecular mass plasmid and virulence in a strain of Salmonella pullorum. J Gen Microbiol. 1988 Aug;134(8):2307–2316. doi: 10.1099/00221287-134-8-2307. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beninger P. R., Chikami G., Tanabe K., Roudier C., Fierer J., Guiney D. G. Physical and genetic mapping of the Salmonella dublin virulence plasmid pSDL2. Relationship to plasmids from other Salmonella strains. J Clin Invest. 1988 May;81(5):1341–1347. doi: 10.1172/JCI113461. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown D. J., Threlfall E. J., Hampton M. D., Rowe B. Molecular characterization of plasmids in Salmonella enteritidis phage types. Epidemiol Infect. 1993 Apr;110(2):209–216. doi: 10.1017/s0950268800068126. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chowdry N., Threlfall E. J., Rowe B., Stanley J. Genotype analysis of faecal and blood isolates of Salmonella dublin from humans in England and Wales. Epidemiol Infect. 1993 Apr;110(2):217–225. doi: 10.1017/s0950268800068138. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Helmuth R., Stephan R., Bunge C., Hoog B., Steinbeck A., Bulling E. Epidemiology of virulence-associated plasmids and outer membrane protein patterns within seven common Salmonella serotypes. Infect Immun. 1985 Apr;48(1):175–182. doi: 10.1128/iai.48.1.175-182.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones G. W., Rabert D. K., Svinarich D. M., Whitfield H. J. Association of adhesive, invasive, and virulent phenotypes of Salmonella typhimurium with autonomous 60-megadalton plasmids. Infect Immun. 1982 Nov;38(2):476–486. doi: 10.1128/iai.38.2.476-486.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawahara K., Haraguchi Y., Tsuchimoto M., Terakado N., Danbara H. Evidence of correlation between 50-kilobase plasmid of Salmonella choleraesuis and its virulence. Microb Pathog. 1988 Feb;4(2):155–163. doi: 10.1016/0882-4010(88)90057-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Montenegro M. A., Morelli G., Helmuth R. Heteroduplex analysis of Salmonella virulence plasmids and their prevalence in isolates of defined sources. Microb Pathog. 1991 Dec;11(6):391–397. doi: 10.1016/0882-4010(91)90035-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakamura M., Sato S., Ohya T., Suzuki S., Ikeda S. Possible relationship of a 36-megadalton Salmonella enteritidis plasmid to virulence in mice. Infect Immun. 1985 Mar;47(3):831–833. doi: 10.1128/iai.47.3.831-833.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olsen J. E., Baggesen D. L., Nielsen B. B., Larsen H. E. The prevalence of plasmids in Danish bovine and human isolates of Salmonella dublin. APMIS. 1990 Aug;98(8):735–740. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1990.tb04994.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Platt D. J., Brown D. J., Munro D. S. The distribution of plasmids among a representative collection of Scottish strains of Salmonellae. J Hyg (Lond) 1986 Oct;97(2):199–204. doi: 10.1017/s002217240006527x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Platt D. J., Taggart J., Heraghty K. A. Molecular divergence of the serotype-specific plasmid (pSLT) among strains of Salmonella typhimurium of human and veterinary origin and comparison of pSLT with the serotype specific plasmids of S. enteritidis and S. dublin. J Med Microbiol. 1988 Dec;27(4):277–284. doi: 10.1099/00222615-27-4-277. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plikaytis B. D., Carlone G. M., Edmonds P., Mayer L. W. Robust estimation of standard curves for protein molecular weight and linear-duplex DNA base-pair number after gel electrophoresis. Anal Biochem. 1986 Feb 1;152(2):346–364. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(86)90420-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selander R. K., Smith N. H., Li J., Beltran P., Ferris K. E., Kopecko D. J., Rubin F. A. Molecular evolutionary genetics of the cattle-adapted serovar Salmonella dublin. J Bacteriol. 1992 Jun;174(11):3587–3592. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.11.3587-3592.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Terakado N., Sekizaki T., Hashimoto K., Naitoh S. Correlation between the presence of a fifty-megadalton plasmid in Salmonella dublin and virulence for mice. Infect Immun. 1983 Jul;41(1):443–444. doi: 10.1128/iai.41.1.443-444.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Threlfall E. J., Rowe B., Ferguson J. L., Ward L. R. Increasing incidence of resistance to gentamicin and related aminoglycosides in Salmonella typhimurium phage type 204c in England, Wales and Scotland. Vet Rec. 1985 Oct 5;117(14):355–357. doi: 10.1136/vr.117.14.355. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williamson C. M., Baird G. D., Manning E. J. A common virulence region on plasmids from eleven serotypes of Salmonella. J Gen Microbiol. 1988 Apr;134(4):975–982. doi: 10.1099/00221287-134-4-975. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woodward M. J., McLaren I., Wray C. Distribution of virulence plasmids within Salmonellae. J Gen Microbiol. 1989 Mar;135(3):503–511. doi: 10.1099/00221287-135-3-503. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woodward M. J., McLaren I., Wray C. Genetic evidence for a chromosomally integrated multiresistance plasmid in Salmonella dublin. J Med Microbiol. 1989 Mar;28(3):205–210. doi: 10.1099/00222615-28-3-205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]