Abstract
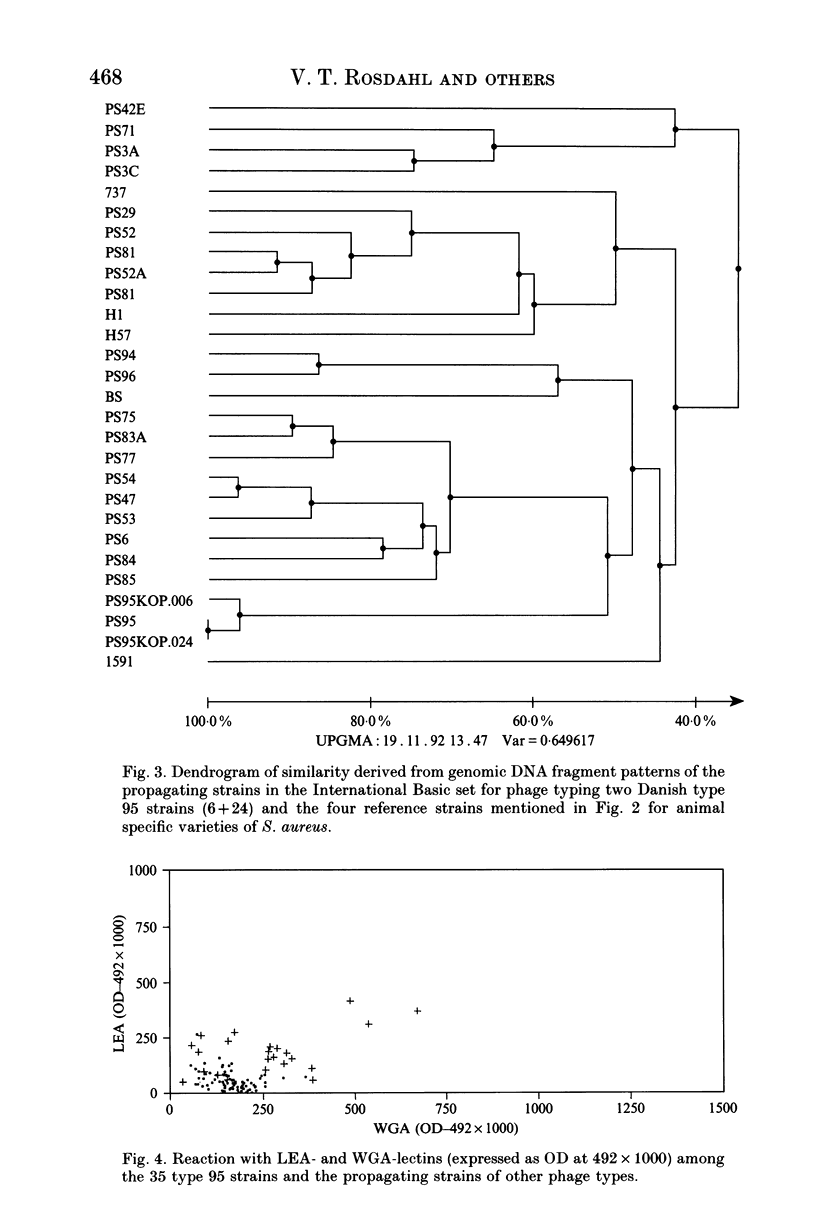
Staphylococcus aureus strains of type 95 in Denmark have increased to a frequency of 20% of the total S. aureus population. A clonal origin and possible subdivision of these strains have been discussed. In the present investigation 35 epidemiologically unrelated S. aureus strains of type 95 as well as reference strains of other types have been analysed by other typing techniques including lectin-typing, multilocus enzyme electrophoresis and pulsed-field gel electrophoresis of genomic restriction fragments. No subdivision could be achieved based on any of these methods and a clonal origin seems therefore possible.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Altemeier W. A., Lewis S. A. Cyclic variations in emerging phage types and antibiotic resistance of Staphylococcus aureus. Surgery. 1978 Oct;84(4):534–541. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Asheshov E. H., Winkler K. C. Staphylococcus aureus strains in the "52, 52A, 80, 81 complex". Nature. 1966 Feb 5;209(5023):638–639. doi: 10.1038/209638b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jarløv J. O., Hansen J. E., Rosdahl V. T., Espersen F. The typing of Staphylococcus epidermidis by a lectin-binding assay. J Med Microbiol. 1992 Sep;37(3):195–200. doi: 10.1099/00222615-37-3-195. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jarløv J. O., Rosdahl V. T., Yeo M., Marples R. R. Lectin typing of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus from Singapore, England and Wales, and Denmark. J Med Microbiol. 1993 Oct;39(4):305–309. doi: 10.1099/00222615-39-4-305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jevons M. P., John M., Parker M. T. Cultural characters of a newly recognized group of hospital staphylococci. J Clin Pathol. 1966 Jul;19(4):305–312. doi: 10.1136/jcp.19.4.305. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Musser J. M., Schlievert P. M., Chow A. W., Ewan P., Kreiswirth B. N., Rosdahl V. T., Naidu A. S., Witte W., Selander R. K. A single clone of Staphylococcus aureus causes the majority of cases of toxic shock syndrome. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jan;87(1):225–229. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.1.225. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosdahl V. T., Knudsen A. M. The decline of methicillin resistance among Danish Staphylococcus aureus strains. Infect Control Hosp Epidemiol. 1991 Feb;12(2):83–88. doi: 10.1086/646291. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosdahl V. T., Laursen H., Bentzon M. W., Kjaeldgaard P., Thomsen M. Colonization priority among Staphylococcus aureus strains--correlation with phage-type. J Hosp Infect. 1988 Oct;12(3):151–162. doi: 10.1016/0195-6701(88)90002-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosdahl V. T., Rosendal K. Unusual properties of Staphylococcus aureus strains of the new epidemic phage type 95. J Med Microbiol. 1985 Dec;20(3):325–333. doi: 10.1099/00222615-20-3-325. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schønheyder H., Jensen K. T., Pers C., Korsager B., Rosdahl V. T. Spread of Staphylococcus aureus strains of phage-type 95 in Denmark 1968-1989. J Hosp Infect. 1992 Jan;20(1):25–34. doi: 10.1016/0195-6701(92)90058-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Witte W., Grimm H. Occurrence of quinolone resistance in Staphylococcus aureus from nosocomial infection. Epidemiol Infect. 1992 Dec;109(3):413–421. doi: 10.1017/s0950268800050408. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Witte W., Hummel R., Meyer W., Exner H., Wundrak R. Ecology of Staphylococcus aureus: characterization of strains from chicken. Z Allg Mikrobiol. 1977;17(8):639–646. doi: 10.1002/jobm.3630170809. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]