Abstract
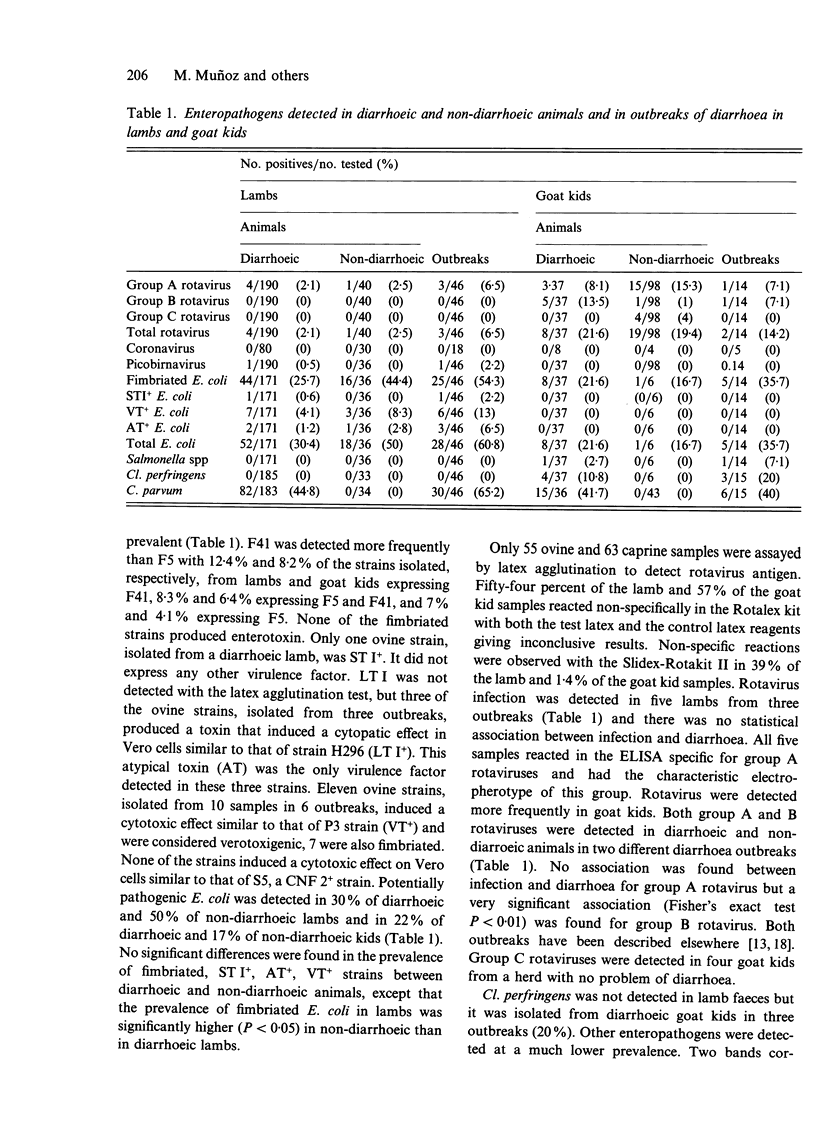
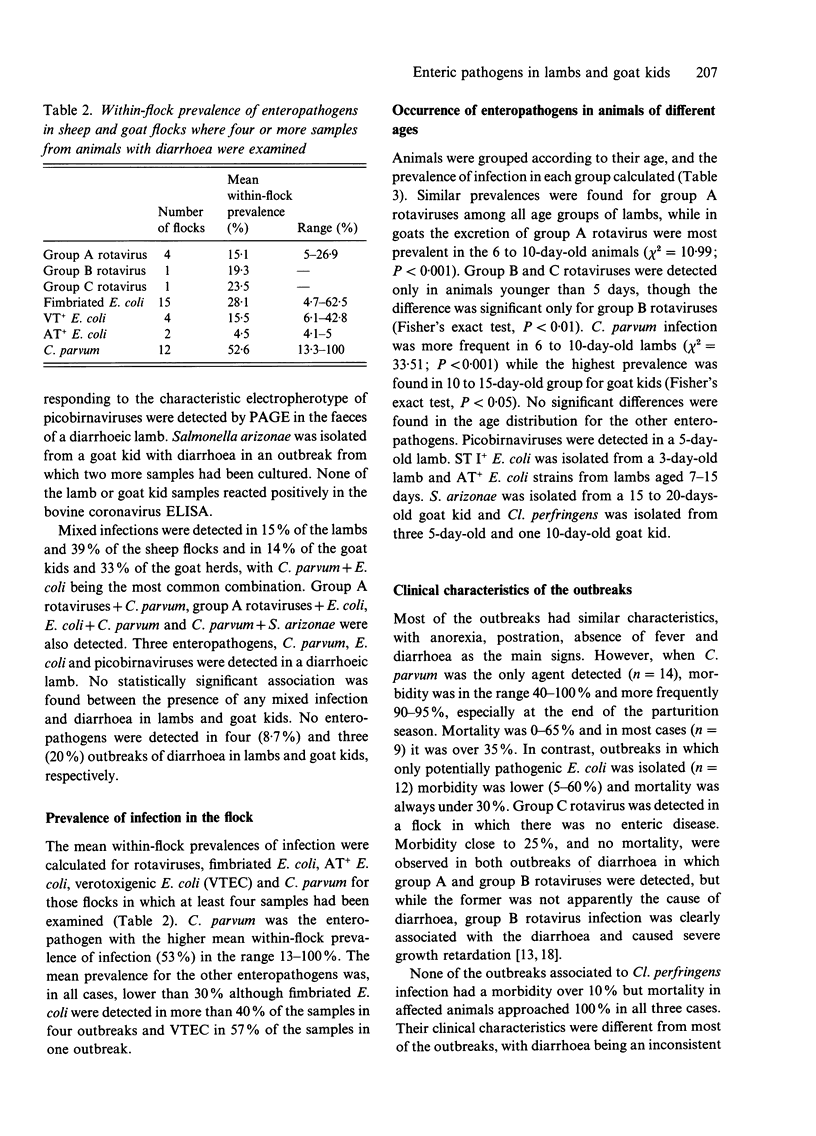
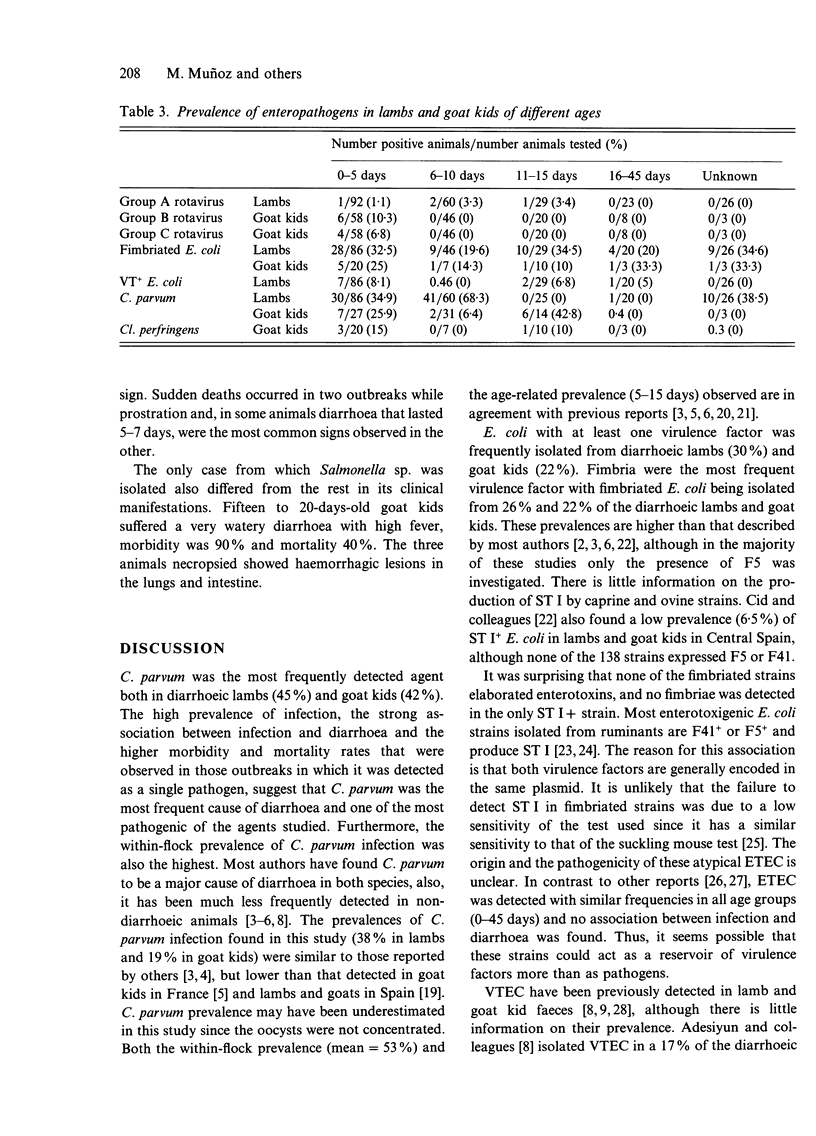
Faeces samples from diarrhoeic and non-diarrhoeic lambs and goat kids aged 1-45 days were examined for enteric pathogens. Cryptosporidium parvum was detected in both diarrhoeic lambs (45%) and goat kids (42%) but not in non-diarrhoeic animals. F5+ (K99+) and/or F41+ Escherichia coli strains were isolated from 26% and 22% of the diarrhoeic lambs and goat kids, respectively, although these strains, which did not produce enterotoxins ST I or LT I, were found with similar frequencies in non-diarrhoeic animals. A F5-F41-ST I+ E. coli strain was isolated from a diarrhoeic lamb (0.6%). Verotoxigenic E. coli was isolated from both diarrhoeic and non-diarrhoeic lambs (4.1% and 8.2%, respectively) and there was no association between infection and diarrhoea. The prevalence of group A rotavirus infection in diarrhoeic lambs was very low (2.1%). Groups A and B rotaviruses were detected in three (8.1%) and five (13.5%) diarrhoeic goat kids from two single outbreaks. Group C rotaviruses were detected in four non-diarrhoeic goat kids. An association of diarrhoea and infection was demonstrated only for group B rotavirus. Clostridium perfringens was isolated from 10.8% of the diarrhoeic goat kids but not from non-diarrhoeic goat kids or lambs. Salmonella arizonae was isolated from a diarrhoeic goat kid (2.7%) and the clinical characteristics of the outbreaks where these two latter enteropathogens were found different from the rest. Picobirnaviruses were detected in a diarrhoeic lamb. No coronaviruses were detected using a bovine coronavirus ELISA. No evidence was found of synergistic effect between the agents studied. Enteric pathogens were not found in four (8.7%) and three (20%) outbreaks of diarrhoea in lambs and goat kids, respectively.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Beutin L., Geier D., Steinrück H., Zimmermann S., Scheutz F. Prevalence and some properties of verotoxin (Shiga-like toxin)-producing Escherichia coli in seven different species of healthy domestic animals. J Clin Microbiol. 1993 Sep;31(9):2483–2488. doi: 10.1128/jcm.31.9.2483-2488.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carroll P. J., Woodward M. J., Wray C. Detection of LT and STIa toxins by latex and EIA tests. Vet Rec. 1990 Sep 29;127(13):335–336. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chanter N., Morgan J. H., Bridger J. C., Hall G. A., Reynolds D. J. Dysentery in gnotobiotic calves caused by atypical Escherichia coli. Vet Rec. 1984 Jan 21;114(3):71–71. doi: 10.1136/vr.114.3.71. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chasey D., Banks J. The commonest rotaviruses from neonatal lamb diarrhoea in England and Wales have atypical electropherotypes. Vet Rec. 1984 Sep 29;115(13):326–327. doi: 10.1136/vr.115.13.326. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cid D., Ruiz Santa Quiteria J. A., de la Fuente R. F17 fimbriae in Escherichia coli from lambs and kids. Vet Rec. 1993 Mar 6;132(10):251–251. doi: 10.1136/vr.132.10.251. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dorn C. R., Scotland S. M., Smith H. R., Willshaw G. A., Rowe B. Properties of Vero cytotoxin-producing Escherichia coli of human and animal origin belonging to serotypes other than O157:H7. Epidemiol Infect. 1989 Aug;103(1):83–95. doi: 10.1017/s0950268800030387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drolet R., Fairbrother J. M., Vaillancourt D. Attaching and effacing Escherichia coli in a goat with diarrhea. Can Vet J. 1994 Feb;35(2):122–123. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans D. J., Jr, Evans D. G., Gorbach S. L. Production of vascular permeability factor by enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli isolated from man. Infect Immun. 1973 Nov;8(5):725–730. doi: 10.1128/iai.8.5.725-730.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fassi-Fehri M. M., Johnson D. W., Taoudi A., Berrada J. Epidèmiologie des diarrhées à Escherichia coli et à rotavirus chez le veau et l'agneau au Maroc. Ann Rech Vet. 1988;19(1):59–64. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gatti M. S., de Castro A. F., Ferraz M. M., Fialho A. M., Pereira H. G. Viruses with bisegmented double-stranded RNA in pig faeces. Res Vet Sci. 1989 Nov;47(3):397–398. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henriksen S. A., Pohlenz J. F. Staining of cryptosporidia by a modified Ziehl-Neelsen technique. Acta Vet Scand. 1981;22(3-4):594–596. doi: 10.1186/BF03548684. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mainil J. G., Bex F., Jacquemin E., Pohl P., Couturier M., Kaeckenbeeck A. Prevalence of four enterotoxin (STaP, STaH, STb, and LT) and four adhesin subunit (K99, K88, 987P, and F41) genes among Escherichia coli isolates from cattle. Am J Vet Res. 1990 Feb;51(2):187–190. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muñoz M., Alvarez M., Lanza I., Cármenes P. An outbreak of diarrhoea associated with atypical rotaviruses in goat kids. Res Vet Sci. 1995 Sep;59(2):180–182. doi: 10.1016/0034-5288(95)90057-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muñoz M., Lanza I., Alvarez M., Cármenes P. Prevalence of neutralizing antibodies to 9 rotavirus strains representing 7 G-serotypes in sheep sera. Vet Microbiol. 1995 Aug;45(4):351–361. doi: 10.1016/0378-1135(95)00002-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reynolds D. J., Morgan J. H., Chanter N., Jones P. W., Bridger J. C., Debney T. G., Bunch K. J. Microbiology of calf diarrhoea in southern Britain. Vet Rec. 1986 Jul 12;119(2):34–39. doi: 10.1136/vr.119.2.34. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith H. W. A search for transmissible pathogenic characters in invasive strains of Escherichia coli: the discovery of a plasmid-controlled toxin and a plasmid-controlled lethal character closely associated, or identical, with colicine V. J Gen Microbiol. 1974 Jul;83(0):95–111. doi: 10.1099/00221287-83-1-95. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snodgrass D. R., Herring J. A., Linklater K. A., Dyson D. A. A survey of rotaviruses in sheep in Scotland. Vet Rec. 1977 Apr 16;100(16):341–341. doi: 10.1136/vr.100.16.341-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snodgrass D. R., Herring J. A., Reid H. W., Scott F. M., Gray E. W. Virus infections in cattle and sheep in Scotland 1975-1978. Vet Rec. 1980 Mar 1;106(9):193–194. doi: 10.1136/vr.106.9.193. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snodgrass D. R., Terzolo H. R., Sherwood D., Campbell I., Menzies J. D., Synge B. A. Aetiology of diarrhoea in young calves. Vet Rec. 1986 Jul 12;119(2):31–34. doi: 10.1136/vr.119.2.31. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tzipori S. R., Makin T. J., Smith M. L., Krautil F. L. Clinical manifestations of diarrhea in calves infected with rotavirus and enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli. J Clin Microbiol. 1981 Jun;13(6):1011–1016. doi: 10.1128/jcm.13.6.1011-1016.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tzipori S., Larsen J., Smith M., Luefl R. U. Diarrhoea in goat kids attributed to cryptosporidium infection. Vet Rec. 1982 Jul 10;111(2):35–36. doi: 10.1136/vr.111.2.35. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tzipori S., Sherwood D., Angus K. W., Campbell I., Gordon M. Diarrhea in lambs: experimental infections with enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli, rotavirus, and Cryptosporidium sp. Infect Immun. 1981 Aug;33(2):401–406. doi: 10.1128/iai.33.2.401-406.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vanopdenbosch E., Wellemans G. Birna-type virus in diarrhoeic calf faeces. Vet Rec. 1989 Dec 9;125(24):610–610. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woodward M. J., Wray C. Nine DNA probes for detection of toxin and adhesin genes in Escherichia coli isolated from diarrhoeal disease in animals. Vet Microbiol. 1990 Oct;25(1):55–65. doi: 10.1016/0378-1135(90)90093-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


