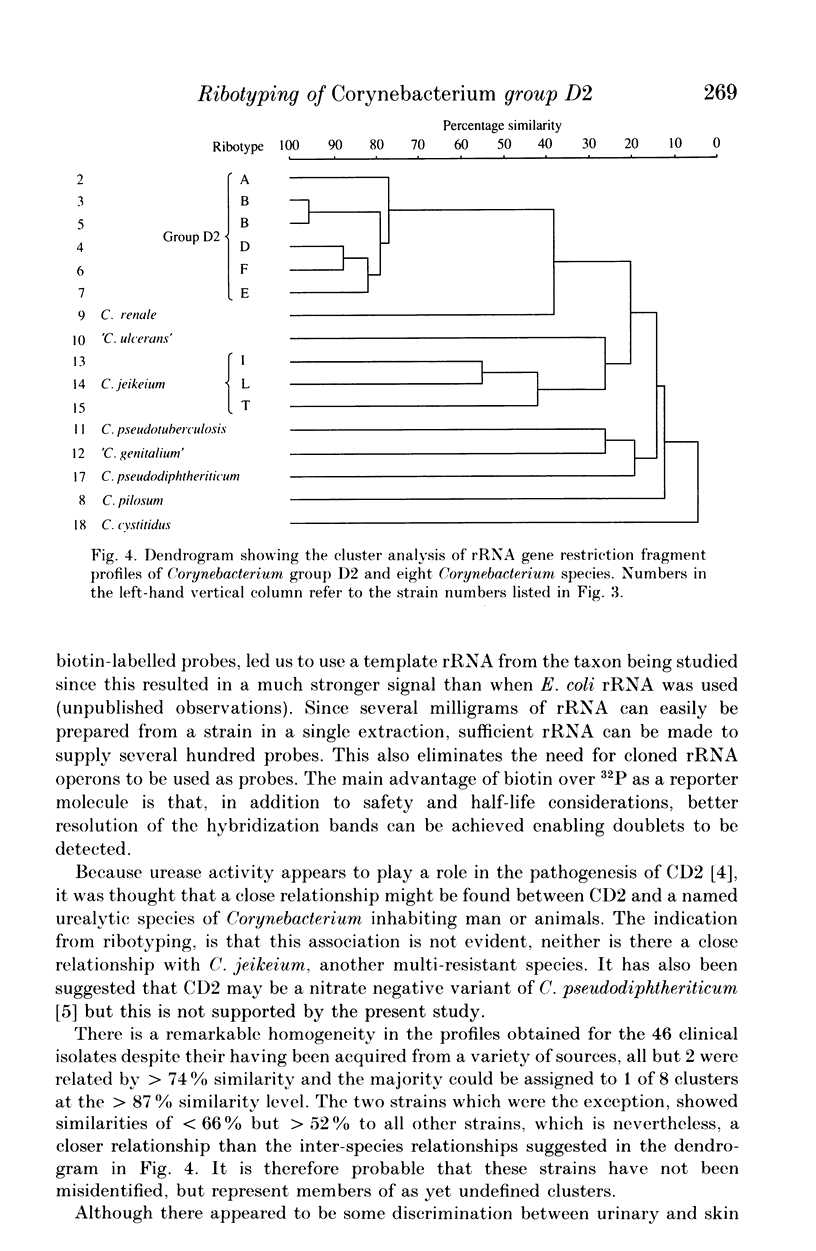
Abstract
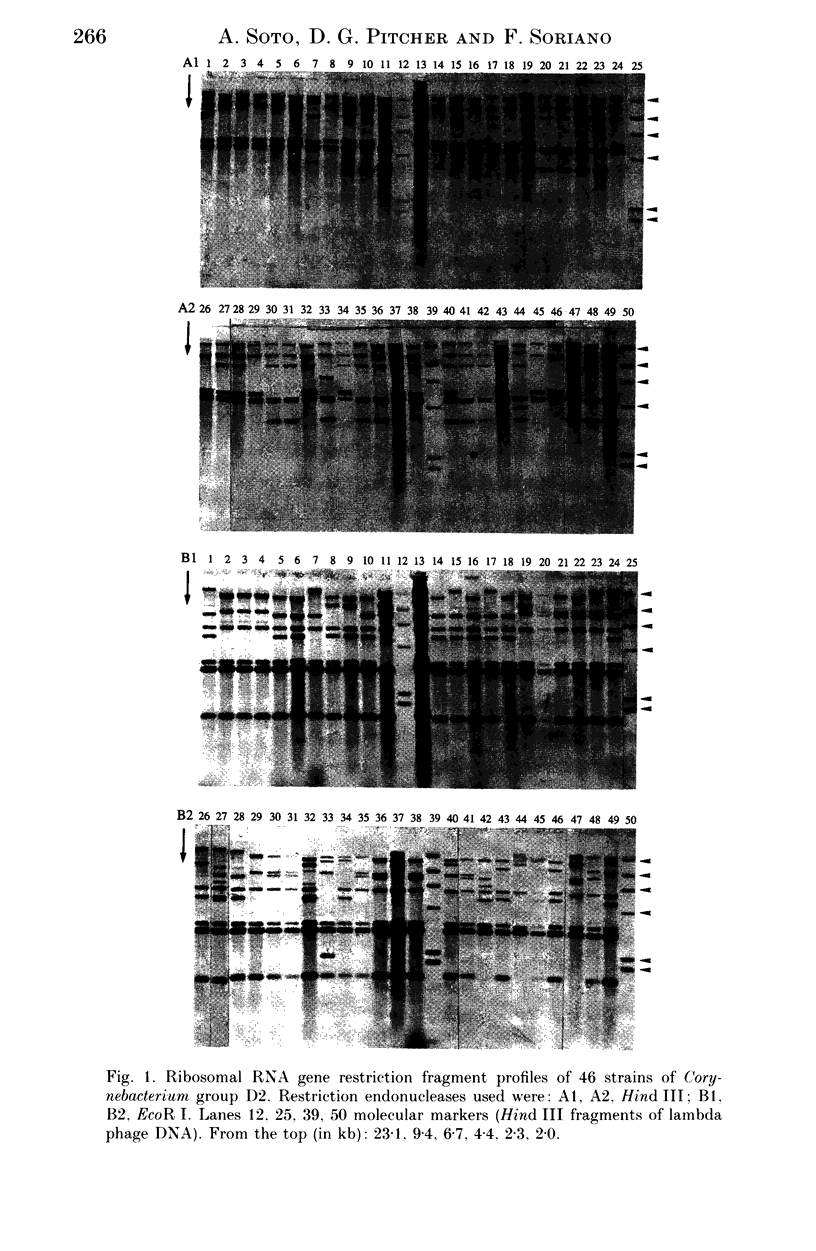
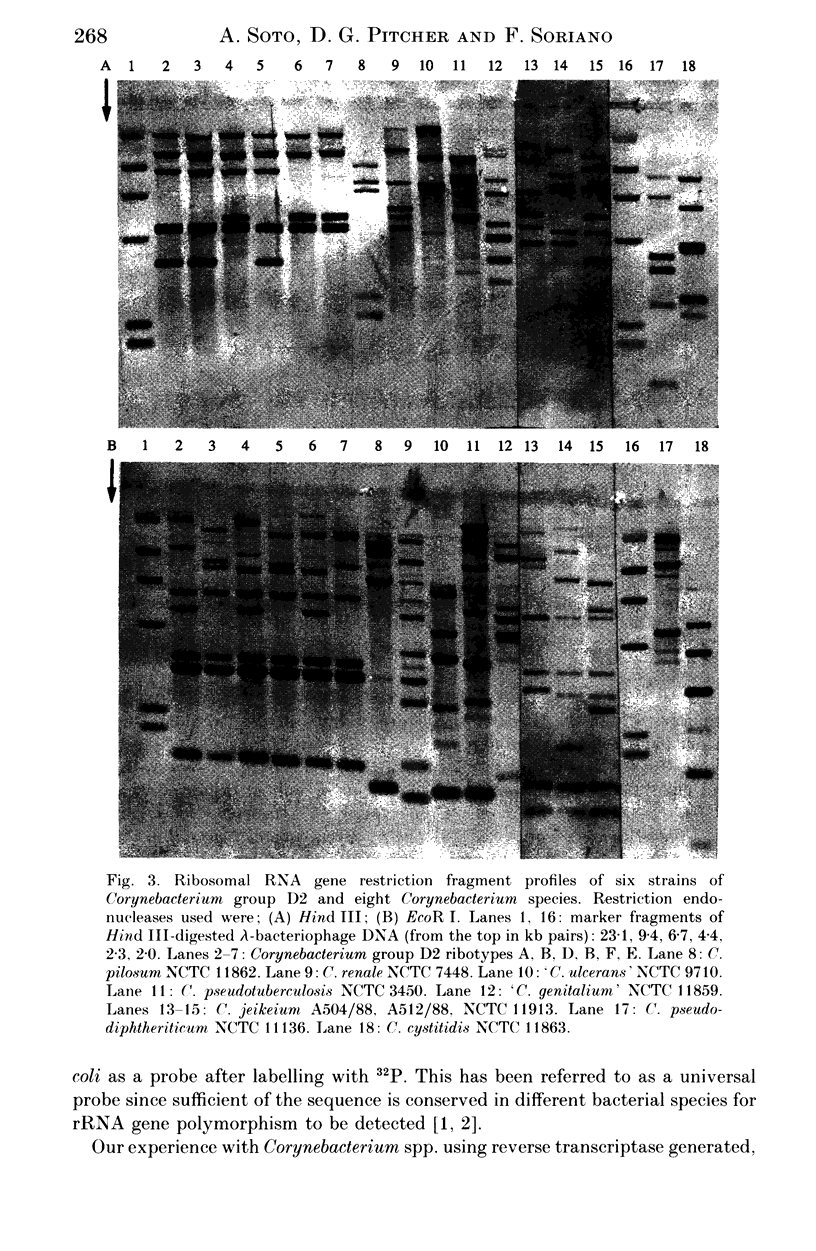
Restriction digest fragments of DNA from 46 clinical isolates identified as Corynebacterium group D2, were separated by electrophoresis, Southern blotted onto nylon membranes and hybridized to a ribosomal RNA gene probe. The resulting band patterns were subjected to unweighed pair-group cluster analysis. Representative strains from the main clusters were compared with similarly prepared band patterns from type strains of human Corynebacterium species. The results indicate that strains identified as Corynebacterium group D2 represent a unique taxon and that computer-assisted analysis of rRNA gene restriction fragment polymorphism (ribotyping) could be a useful technique in epidemiological studies of these bacteria.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Coyle M. B., Lipsky B. A. Coryneform bacteria in infectious diseases: clinical and laboratory aspects. Clin Microbiol Rev. 1990 Jul;3(3):227–246. doi: 10.1128/cmr.3.3.227. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evangelista A. T., Coppola K. M., Furness G. Relationship between group JK corynebacteria and the biotypes of Corynebacterium genitalium and Corynebacterium pseudogenitalium. Can J Microbiol. 1984 Aug;30(8):1052–1057. doi: 10.1139/m84-164. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freney J., Duperron M. T., Courtier C., Hansen W., Allard F., Boeufgras J. M., Monget D., Fleurette J. Evaluation of API Coryne in comparison with conventional methods for identifying coryneform bacteria. J Clin Microbiol. 1991 Jan;29(1):38–41. doi: 10.1128/jcm.29.1.38-41.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grimont F., Grimont P. A. Ribosomal ribonucleic acid gene restriction patterns as potential taxonomic tools. Ann Inst Pasteur Microbiol. 1986 Sep-Oct;137B(2):165–175. doi: 10.1016/s0769-2609(86)80105-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herrera-Alcaraz E. A., Valero-Guillén P. L., Martín-Luengo F., Soriano F. Taxonomic implications of the chemical analysis of the D2 group of corynebacteria. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 1990 Nov;60(3):341–344. doi: 10.1016/0378-1097(90)90328-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hindmarch J. M., Magee J. T., Hadfield M. A., Duerden B. I. A pyrolysis-mass spectrometry study of Corynebacterium spp. J Med Microbiol. 1990 Feb;31(2):137–149. doi: 10.1099/00222615-31-2-137. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Irino K., Grimont F., Casin I., Grimont P. A. rRNA gene restriction patterns of Haemophilus influenzae biogroup aegyptius strains associated with Brazilian purpuric fever. J Clin Microbiol. 1988 Aug;26(8):1535–1538. doi: 10.1128/jcm.26.8.1535-1538.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nadal D., Schwöbel M., von Graevenitz A. Corynebacterium group D2 and urolithiasis in a boy with megacalycosis. Infection. 1988 Jul-Aug;16(4):245–247. doi: 10.1007/BF01650763. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Owen R. J. Chromosomal DNA fingerprinting--a new method of species and strain identification applicable to microbial pathogens. J Med Microbiol. 1989 Oct;30(2):89–99. doi: 10.1099/00222615-30-2-89. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pitcher D., Johnson A., Allerberger F., Woodford N., George R. An investigation of nosocomial infection with Corynebacterium jeikeium in surgical patients using a ribosomal RNA gene probe. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 1990 Sep;9(9):643–648. doi: 10.1007/BF01964264. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soriano F., Aguado J. M., Ponte C., Fernández-Roblas R., Rodríguez-Tudela J. L. Urinary tract infection caused by Corynebacterium group D2: report of 82 cases and review. Rev Infect Dis. 1990 Nov-Dec;12(6):1019–1034. doi: 10.1093/clinids/12.6.1019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soriano F., Fernández-Roblas R. Infections caused by antibiotic-resistant Corynebacterium group D2. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 1988 Jun;7(3):337–341. doi: 10.1007/BF01962333. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soriano F., Rodriguez-Tudela J. L., Fernández-Roblas R., Aguado J. M., Santamaría M. Skin colonization by Corynebacterium groups D2 and JK in hospitalized patients. J Clin Microbiol. 1988 Sep;26(9):1878–1880. doi: 10.1128/jcm.26.9.1878-1880.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stull T. L., LiPuma J. J., Edlind T. D. A broad-spectrum probe for molecular epidemiology of bacteria: ribosomal RNA. J Infect Dis. 1988 Feb;157(2):280–286. doi: 10.1093/infdis/157.2.280. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tillotson G., Arora M., Robbins M., Holton J. Identification of Corynebacterium jeikeium and Corynebacterium CDC group D2 with the API 20 Strep system. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 1988 Oct;7(5):675–678. doi: 10.1007/BF01964252. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Bosterhaut B., Claeys G., Gigi J., Wauters G. Isolation of Corynebacterium group D2 from clinical specimens. Eur J Clin Microbiol. 1987 Aug;6(4):418–419. doi: 10.1007/BF02013099. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]