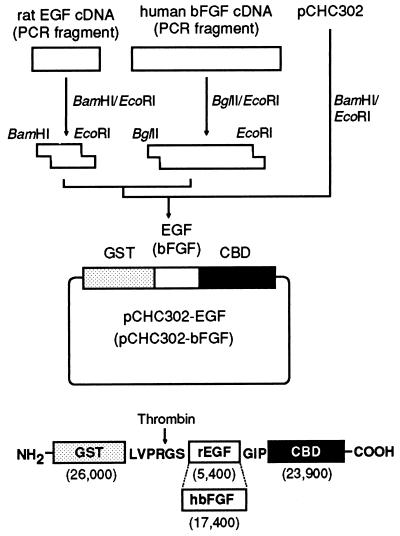
Figure 1.
Scheme for the construction of the expression plasmids and the structures of their translation products. cDNAs for rat EGF and human bFGF were amplified by PCR from first-strand cDNAs prepared from the poly(A)+ RNA fraction of rat submaxillary gland and a human osteosarcoma cell line, respectively, using primers tagged with extra 5′ restriction sites. Each amplified cDNA was digested with restriction enzymes and then inserted into the BamHI–EcoRI site of pCHC302, giving pCHC302-EGF and pCHC302-bFGF, which express fusion proteins between GST and collagen-binding EGF (GST-CBEGF) and collagen-binding bFGF (GST-CBFGF), respectively. In the structure of GST-CBEGF (GST-CBFGF), amino acid residues derived from the pGEX-4T-2 plasmid vector are given in the single-letter code, and the thrombin-cleavage site is indicated by an arrow. The numbers in parentheses are the molecular weights of the domains.