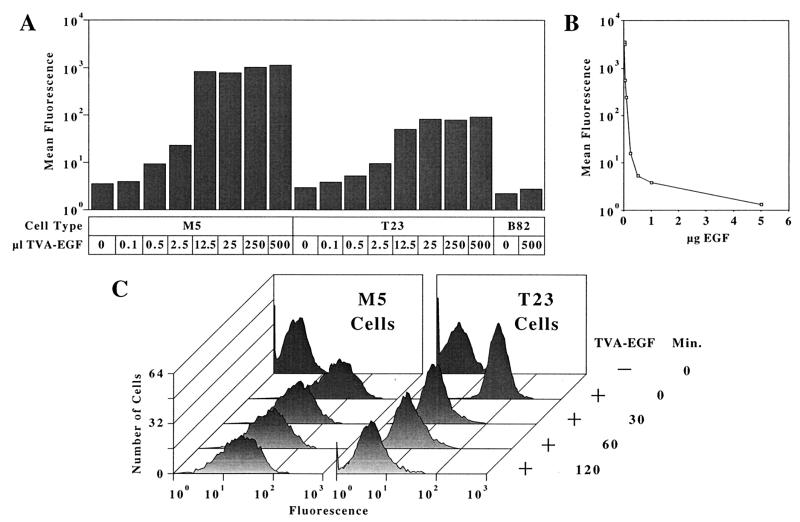
Figure 2.
TVA-EGF binds specifically to the ligand-binding regions of cell surface EGFRs. (A) TVA-EGF binds in a saturable manner to M5 and to T23 cells. B82 mouse L cells lacking EGFRs, M5 cells expressing kinase-deficient human EGFRs, or T23 cells expressing wild-type human EGFRs (12, 13), were incubated with the indicated amounts of extracellular supernatants that contained TVA-EGF. The cells were then incubated with SUA-rIgG (11) and with fluorescein isothiocyanate-conjugated antibodies specific for rabbit Igs and analyzed by flow cytometry. Mean fluorescence values obtained with each cell population are shown. (B) EGF competes for TVA-EGF binding to M5 cells. M5 cells were incubated with extracellular supernatants containing TVA-EGF and increasing amounts of a recombinant human EGF protein. The level of cell surface-associated TVA-EGF in each cell population was measured by flow cytometry as described above. The data shown is representative of two independent experiments that were each performed in triplicate. (C) TVA-EGF disappeared more rapidly from the surfaces of T23 as opposed to M5 cells. M5 and T23 cells were preincubated at 4°C with extracellular supernatants that either lacked or contained TVA-EGF and then transferred to 37°C for the indicated periods of time. The TVA-EGF proteins that remained on the cell surface at each time point were detected by flow cytometry as described above. The data shown is representative of results obtained from three independent experiments.