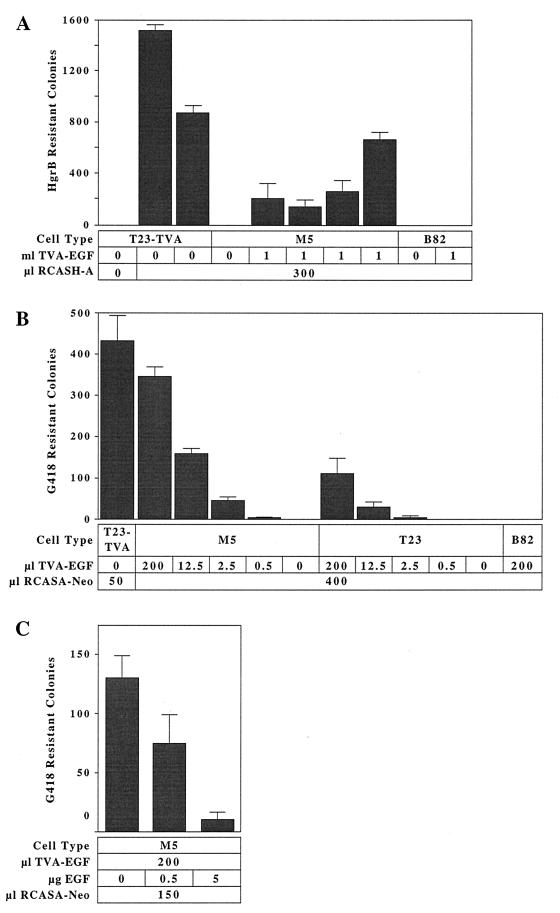
Figure 3.
The TVA-EGF protein mediates ALV-A infection when attached to cell surface EGFRs. (A) B82 and M5 cells incubated with medium that contained or lacked TVA-EGF, and T23TVA cells expressing a transmembrane form of TVA, were challenged with the subgroup A specific RCASH-A virus encoding hygromycin B phosphotransferase (7). The numbers of hygromycin B-resistant colonies, representing individual infection events, were counted and the results of independent experiments, each performed in triplicate, are shown. (B) B82, T23 and M5 cells were incubated with medium containing the indicated amounts of TVA-EGF and then challenged with the subgroup A-specific RCASA-Neo virus encoding neomycin phosphotransferase (2). The number of infected G418-resistant colonies was determined. T23TVA cells were also challenged with this virus, and the average number of infected G418-resistant colonies was determined after subtracting the small number of drug-resistant colonies that arose without virus addition (see Materials and Methods). These data are representative of three independent infection experiments that were each performed in triplicate. (C) EGF blocks TVA-EGF-dependent viral entry. M5 cells were incubated with extracellular supernatants containing TVA-EGF in the presence of different amounts of recombinant EGF and then challenged with the RCASA-Neo virus. The resulting G418-resistant infected colonies were counted, and the average numbers from two independent experiments that were each performed in triplicate are shown.