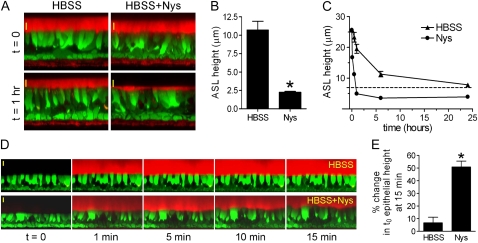
Figure 4.
Acute Nys challenge promotes mucosal volume absorption in HBEs and induces cell swelling in the presence of large mucosal volume. (A) Representative XZ confocal images of HBEs loaded with Calcein-AM (green signal) and layered with Texas Red–labeled ASL volume (thin film conditions, red signal) in the absence (HBSS) or presence of Nys (HBSS+Nys), at t = 0 (upper panels) and t = 1 hour of incubation in highly humidified incubator (lower panels). Scale bar = 10 μm. (B) Compiled data from thin film measurements of steady state ASL volume. Data are expressed as ASL height and shown as mean ± SEM, n = 4 individual donors, 2 cultures/condition; *P < 0.0001. (C) Kinetic measurements of ASL volume absorption by naïve HBEs in the absence (HBSS) or presence of Nys (Nys). (D) Representative sequence of XZ confocal images of calcein-loaded naive HBEs used for cell swelling measurements upon acute Nys challenge in the presence of large mucosal volume. At t = 1 minute, 200 μl of Texas Red–labeled HBSS (upper panel) or HBSS+Nys (lower panel) were mucosally applied. Scale bar = 10 μm. (E) Compiled data for epithelial cell swelling measured as increase in epithelial height over baseline (t = 0) at 15 minutes. Data are shown as average ± SEM, n = 3 individual donors, 2 cultures/condition; *P < 0.01 versus HBSS.