Table 1.
Similarity between patterns of enhanced coherence
| Verbal
|
Visual
|
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| p | r | p | r | ||
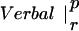 |
1 | ||||
| 0 | 1 | ||||
| δ | 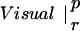 |
0 | 0 | 1 | |
| 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | ||
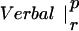 |
1 | ||||
| 0 | 1 | ||||
| θ | 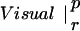 |
0 | 0 | 1 | |
| 0 | 0.35 | 0 | 1 | ||
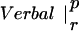 |
1 | ||||
| 0 | 1 | ||||
| α2 | 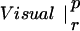 |
0.31 | 0 | 1 | |
| 0 | 0.22 | 0.27 | 1 | ||
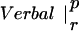 |
1 | ||||
| 0 | 1 | ||||
| α1 | 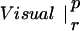 |
0 | 0.11 | 1 | |
| 0 | 0.21 | 0.60 | 1 | ||
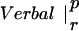 |
1 | ||||
| 0 | 1 | ||||
| β | 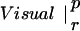 |
0.27 | 0.12 | 1 | |
| 0.40 | 0 | 0.14 | 1 | ||
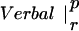 |
1 | ||||
| 0.54 | 1 | ||||
| γ | 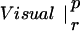 |
0.60 | 0.42 | 1 | |
| 0.41 | 0.42 | 0.52 | 1 | ||
The table compares the EEG coherence patterns of the two task conditions (visual and verbal) in each frequency band for both perception (p) and retention (r). The similarity S between two patterns is quantified as the ratio of equal connections with respect to the total number of connections in both maps. For example, Fig. 3 A and B share eight connections (Fr-T5; Fp2-T5; Fz-T5; Fp1-T5). Dividing by 23, the total number of connections, gives S = 0.35. In θ, the patterns during retention were highly similar but different from all other conditions; in γ, all patterns showed a high degree of similarity. (In the diagonals, patterns are compared to themselves, leading to a similarity of S = 1.)
