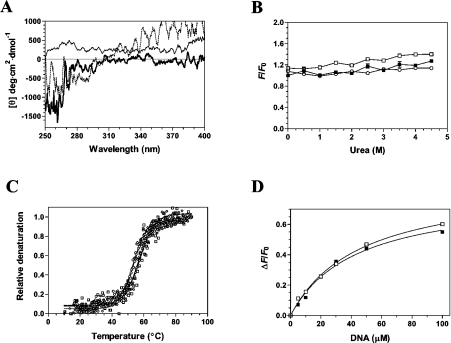
Figure 6. Structural consequences of ligand binding to the cytomegalovirus DNA polymerase.
(A) Near-UV CD spectra were recorded for the unliganded protein (black line), the protein–DNA binary complex (thick line), and the transition state of the enzyme (protein–DNA–dATPαS) (dotted line). Formation of the protein–DNA binary complex was induced by incubating the enzyme (1 μM) with 100 μM DNA (primer template P20/T60). The transition state was generated by adding 1 mM of dATPαS to the binary complex. The spectra were recorded from 250 to 400 nm, and the average of three wavelength scans is presented. (B) Binding of ANS to the cytomegalovirus DNA polymerase during urea denaturation. The unliganded protein (1 μM) (■), binary complex (□) and transition state (○) were unfolded with various concentrations of urea at 22 °C for 1 h. Fluorescence emission was monitored after ANS addition (50 μM) at an excitation wavelength of 380 nm. The integrated fluorescence area between 400 and 600 nm was evaluated. (C) Thermal denaturation of the enzyme. Thermal denaturation was recorded for the unliganded protein (◇), the protein–DNA binary complex (□) or the transition state (○). CD spectra were recorded at a constant wavelength of 222 nm from 10 to 90 °C at a protein concentration of 1 μM. (D) The affinity of the enzyme for the substrate of 30 nt encompassing the cytomegalovirus immediate-early promoter sequence was also monitored in the absence (■) or presence of 1 mM foscarnet (□).