Figure 1.
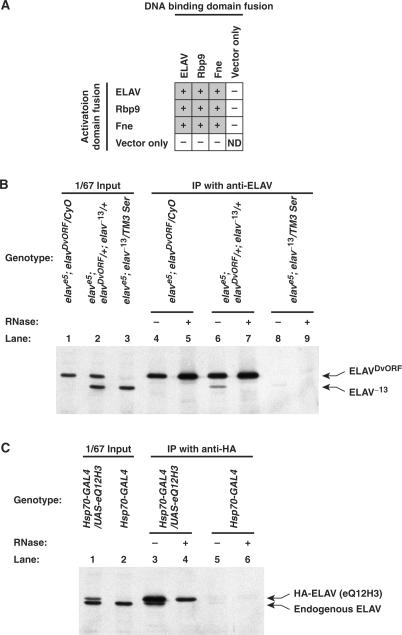
(A) Yeast two-hybrid interactions between Drosophila ELAV-family proteins. In the matrix, ‘+’ and ‘−’ indicate positive and negative interactions in the yeast two-hybrid assay, respectively. The results show that all Drosophila ELAV-family proteins, ELAV, Rbp9 and Fne, interact with themselves as well as each other. ‘Vector only’ means empty pGBKT7 and pGADT7 vectors for the DNA biding and activation domain fusions, respectively. ND, not determined. (B and C) ELAV–ELAV interaction is sensitive to RNase treatment. (B) Both ELAVDvORF and ELAV−13 were expressed in the elav null mutant flies. Immunoprecipitation (IP) was performed with the anti-ELAV mAb 7D which does not recognize ELAV−13, and western blot was probed with the anti-ELAV polyclonal antiserum. ELAV−13 was co-IPed with ELAVDvORF (lane 6), and the co-IPed ELAV−13 became undetectable with RNase treatment (lane 7). The elave5; elavDvORF/CyO (lanes 1, 4 and 5) and elave5; elav−13/TM3 Ser (lanes 3, 8 and 9) are negative controls in which ELAVDvORF and ELAV−13 were solely expressed, respectively. (C) HA-tagged ELAV was expressed in the flies with Hsp70-GAL4 driver, and an anti-HA mAb was used for IP. Western blot was probed with the anti-ELAV polyclonal antiserum. The endogenous ELAV was co-IPed with HA-ELAV (lane 3), and the interaction was disrupted by RNase treatment (lane 4). The Hsp70-GAL4 (lanes 2, 5 and 6) is a negative control that does not have the HA-tagged ELAV (UAS-eQ12H3) transgene.