Figure 2.
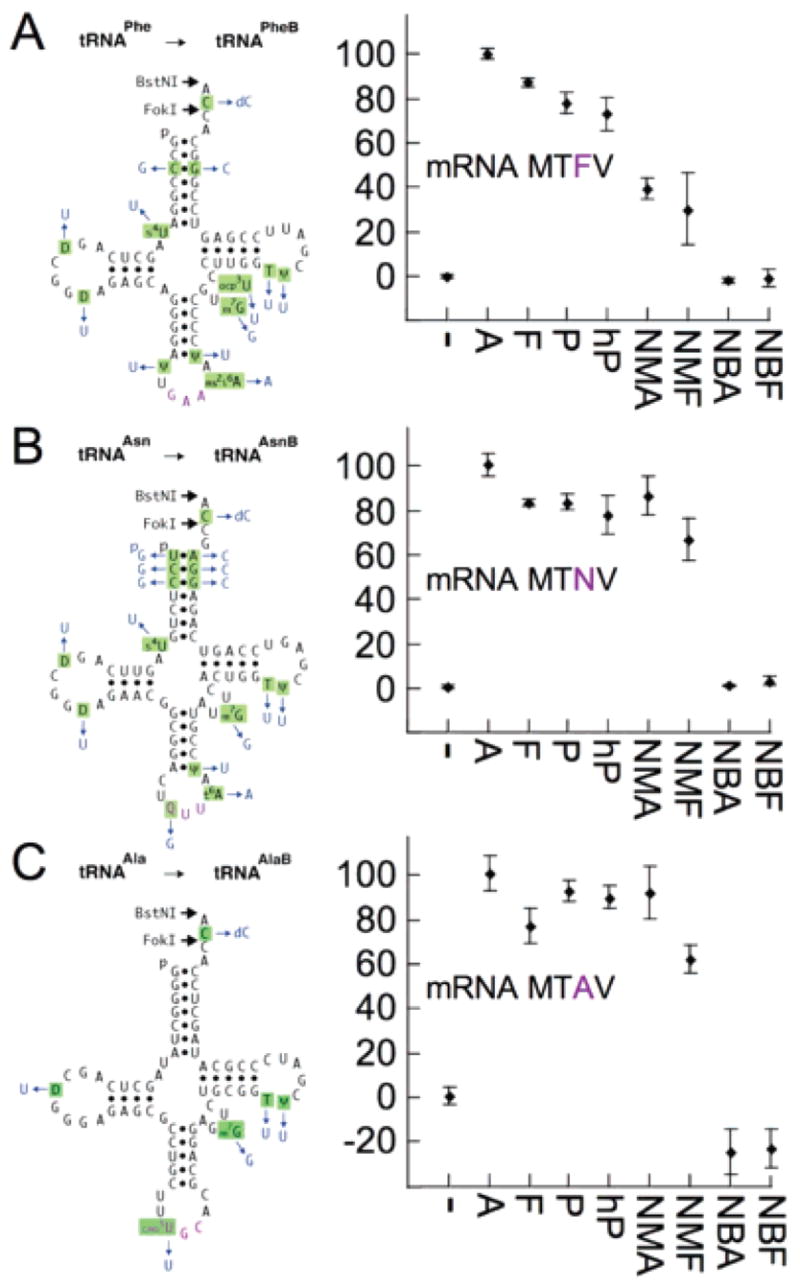
Efficiencies of incorporation of amino/N-alkyl amino acids from synthetic tRNAs into peptide tetramers in the 24 assays of Figure 1. Left: natural E. coli tRNAs (black with purple anticodons) and their synthetic unmodified counterparts (changes in blue). Right: yields of peptide tetramers in pure, synthetase-free translations incubated at 37 °C for 40 min. (−) Background counts defined by omitting cognate aminoacyl-tRNAs for the third codons. Addition of wild-type Phe-tRNAPhe in (A) gave the positive control (95 ± 5%; not plotted). Ala-tRNAPheB gave 100 ± 2%, and the other two Ala-charged unmodified tRNAs also saturated tetrapeptide synthesis (normalized to 100%). Yields with all other substrates were calculated relative to their respective Ala-tRNAs. Standard deviations of quadruplicate experiments are shown. See Supporting Information.
