Table 1.
Structure–activity relationship of the Coumestan analogues
| Compounds | Structure | NS5B inhibition (IC50 μM) | Log P | Gscorea | Gscoreb |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Wedelolactone | 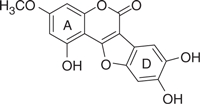 |
36.1 | 0.87 | −7.34 | −6.71 |
| LQB16 | 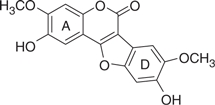 |
311 | 1.70 | −4.61 | −4.72 |
| LQB34 | 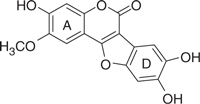 |
18.5 | 0.82 | −7.53 | −6.91 |
| LQB93 | 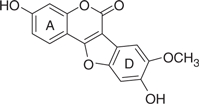 |
174 | 1.52 | −6.63 | −6.32 |
| LQB96 | 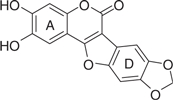 |
63.8 | 0.98 | −6.91 | −6.28 |
The concentration of DMSO in all reactions was kept constant at 10%. The IC50 values of the coumestan analogues were determined from dose–response curves using 8–12 concentrations for each compound in duplicate. Curves were fitted to data points and IC50 values were interpolated from the resulting curves using SigmaPlot 8.0 software. The values represent an average from at least two independent experiments. N,N-disubstituted phenylalanine derivative 14 (IC50 = 0.3 μM) was included as an internal reference standard. The predicted hydrophobicity of the coumestans was determined from their log P values employing QikProp 3.0 program (Schrodinger software package). Gscorea and Gscoreb values were determined by docking of coumestans into NS5B NNI binding site for tetracyclic indole (PDB ID: 2DXS) and N,N-disubstituted phenylalanine (PDB ID: 1NHU), respectively. A more negative Gscore indicates a better fit at the binding site.
