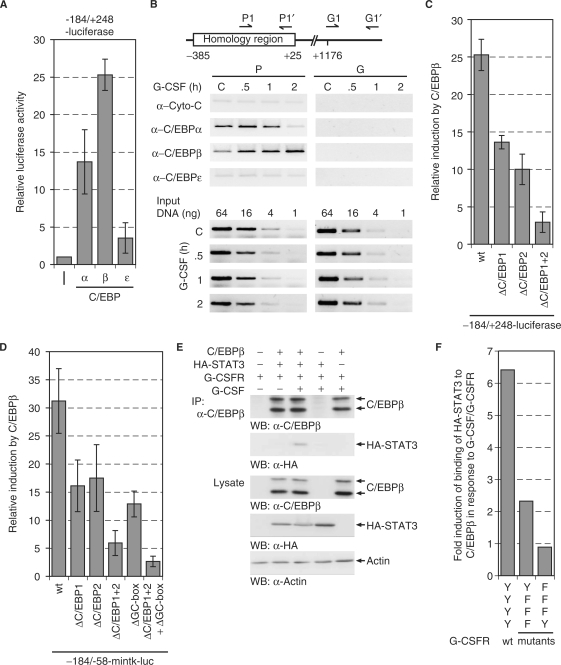
Figure 7.
C/EBP proteins regulate the MAD1 promoter. (A) The –184 to + 248 MAD1 promoter reporter gene construct was cotransfected with plasmids expressing different C/EBP proteins. The mean values and standard deviations of three experiments performed in duplicates are shown. (B) U937 cells were stimulated for the indicated times with G-CSF. The cells were then crosslinked, lyzed and the indicated proteins immunoprecipitated. The associated DNA was analyzed by PCR using primers that correspond to the 3′ portion of the homology region or to a downstream fragment within the MAD1 gene body. For control serial dilutions of input DNA was analyzed by PCR. (C) Transient transfections were performed as described in (A). Reporter constructs with the indicated mutations were used as shown. (D) Transient transfections were performed as described (A) with –184 to –58-mintk promoter constructs and mutants thereof. (E) C/EBPβ, HA-STAT3 and G-CSFR were expressed in HEK293 cells. Prior to harvesting, the cells were treated with or without G-CSF as indicated. C/EBPβ was immunoprecipitated and the associated STAT3 detected by western blotting using an antibody specific for the HA-tag. The lysates show the expression controls. (F) The experimental approach was as in panel E. The relative STAT3 interaction with C/EBPβ upon stimulation with G-CSF and the indicated receptor mutants is displayed.