Figure 1.
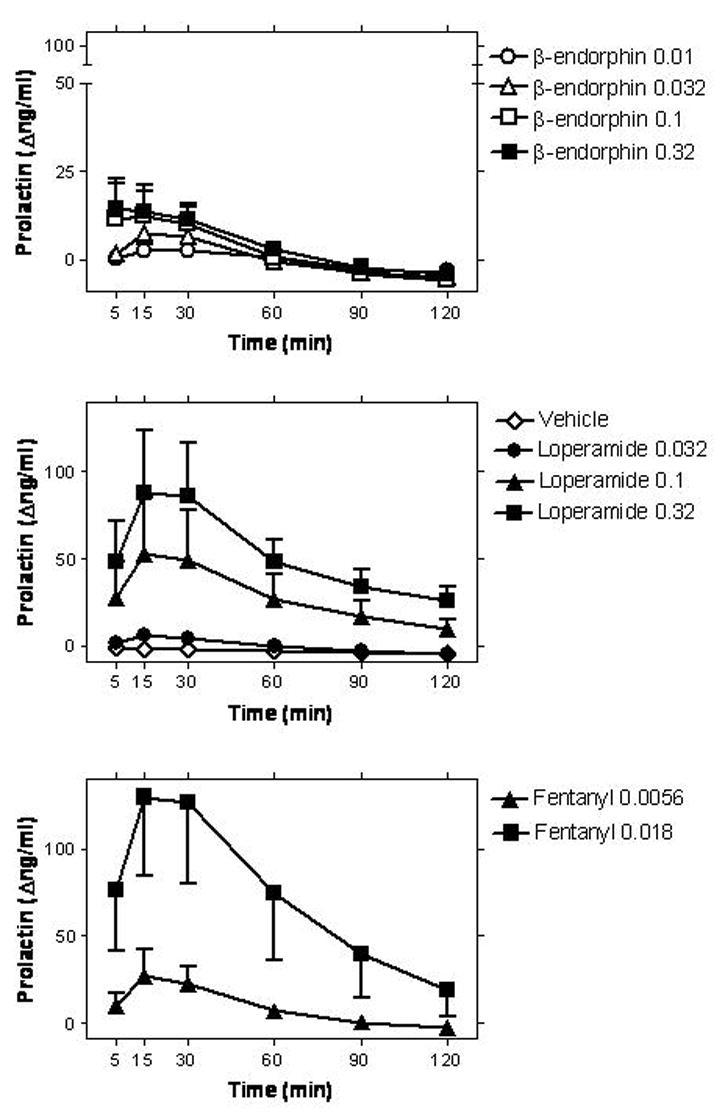
Timecourse of the effects of i.v.β-endorphin (0.01–0.32 mg/kg; upper panel), vehicle or loperamide (0.032–0.32 mg/kg; middle panel), and fentanyl (0.0056–0.018 mg/kg; lower panel) on serum prolactin levels. Data are mean ± SEM (n=4; same subjects used in all studies). Abscissae (all panels) time from i.v. injection. Ordinates (all panels) change in serum prolactin levels (Δng/ml), from the individual pre-injection baseline of each subject (mean of two baseline samples; −10 and −5 min). Note ordinate axis break and axis range in lower panel.
