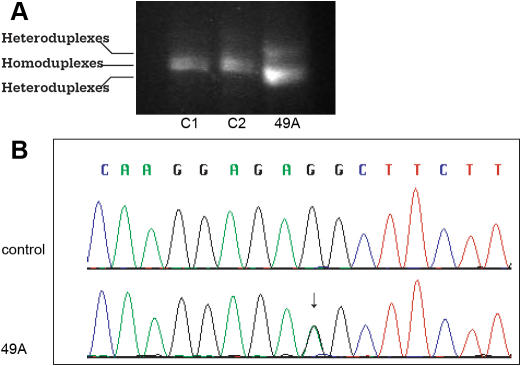
Figure 4.
SOX2 mutation in the 3′- untranslated region (3′-UTR). Genomic DNA from the affected patient and healthy controls are amplified by PCR. PCR products are separated by electrophoresis in an 8% polyacrylamide gel for detection of heteroduplexes and homoduplexes. Genomic DNA samples are then sequenced for detection of sequence variants. A: Heteroduplexes detected by CSGE is shown. Lanes C1 and C2 represent the healthy controls and Lane 49A represents the proband. Sample from patient 49A shows heteroduplex comparing to homoduplex observed in samples from normal controls (C1 and C2). B: A nucleotide substitution at c.*557G>A of the 3′-UTR is identified in patient 49A, but not in normal controls (C). The sequence variant does not predictably change the SOX2 protein and is not a previously described SNP.