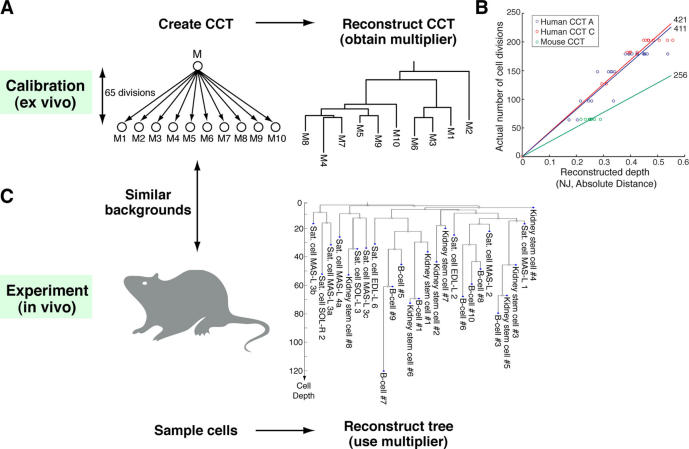
Figure 2. Estimating cell depths from somatic mutations.
(A) Our method for in vivo cell depth estimation employs a calibration system based on a cultured cell tree (CCT) – an ex vivo tree with known topology and well-estimated edge lengths. A CCT created from an Mlh1−/− mouse cell line (of similar background to the mice in which we performed depth analyses) is shown. CCT leaves (M1–M10) were analyzed over a panel of about 100 MS loci, and a tree was reconstructed using the method described in ref. [9] (Neighbor-Joining [NJ] phylogenetic algorithm and ‘Absolute-distance’ distance function were used; see Materials and Methods). Reconstructed depths of all leaves (except for M2, an outlier omitted from analysis) were very similar, with a standard deviation of less than 8% of the mean. (B) Linear correlation between actual and reconstructed depths of human and mouse CCTs. Circles represent CCT nodes; numbers indicate multipliers in each CCT. (C) A multiplier obtained from a CCT is used to calibrate the depths of cells in the reconstructed cell lineage tree.