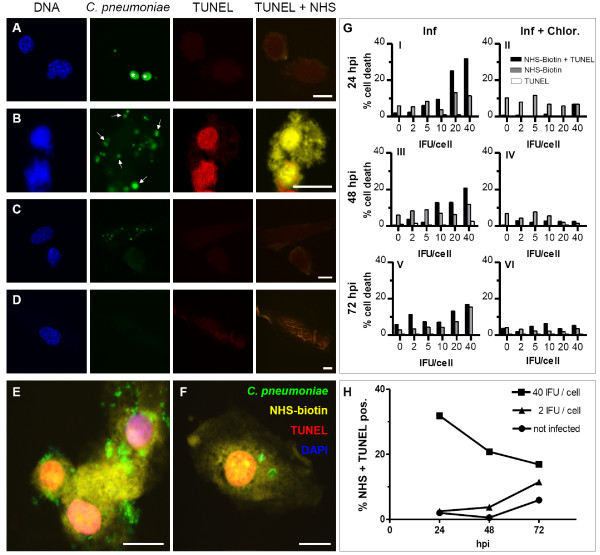
Figure 2.
Cell death morphology of C. pneumoniae infected HAEC. HAEC were infected with C. pneumoniae (A, B, C, E, F) or additionally treated with chloramphenicol (C) or left uninfected (D). C. pneumoniae were detected with anti C. pneumoniae-MOMP (green), DNA strand breaks with TUNEL (red), cytoplasm with NHS-biotin (yellow) and DNA of bacteria and host cells with DAPI (blue). Cells in random fields were counted (n = 200) and the percentage of NHS-biotin-TUNEL positive cells was calculated (G, H). A: HAEC infected with 20 IFU/cell 48 hpi displaying normal nuclear morphology and two MOMP positive inclusions (asterisks). B: HAEC infected with 20 IFU/cell 48 hpi that show a spot-like infection and TUNEL positive condensed nuclei as well as cytoplasmic NHS-biotin signal. C. pneumoniae-MOMP positive spots and aggregates (arrows) are randomly scattered in the cell. C: Chloramphenicol treated cells infected with 20 IFU/cell 48 hpi lack TUNEL and NHS-biotin labelling and display a regular nuclear morphology. D: Uninfected HAEC displaying a regular nuclear structure without TUNEL and cytoplasmic NHS-biotin label. E: HAEC infected for 24 h with 40 IFU/cell. F: HAEC infected for 72 h with 5 IFU/cell. Note that although the cells are infected with different infection doses and fixed at different time points they both elicit the same cell death morphology, thus excluding a cytotoxic effect and underlining the independency of cell death morphology from infection time. Scale bar; 10 μm G (left panel): The number of double positive cells (NHS-biotin + TUNEL) increases dose dependently. The number of single NHS-biotin positive cells does not significantly vary among different infection doses and time points. G (right panel): Chloramphenicol treated infected cells display a lower amount of NHS-biotin-TUNEL positive cells which is independent of the initial infectious dose compared to untreated cells. H: The number of NHS-biotin-TUNEL positive cells increases time dependently in HAEC infected with low infection doses whereas in cells infected with high C. pneumoniae concentrations the number of NHS-biotin-TUNEL positive cells decreases over time. One representative experiment out of three is shown.