Figure 2.
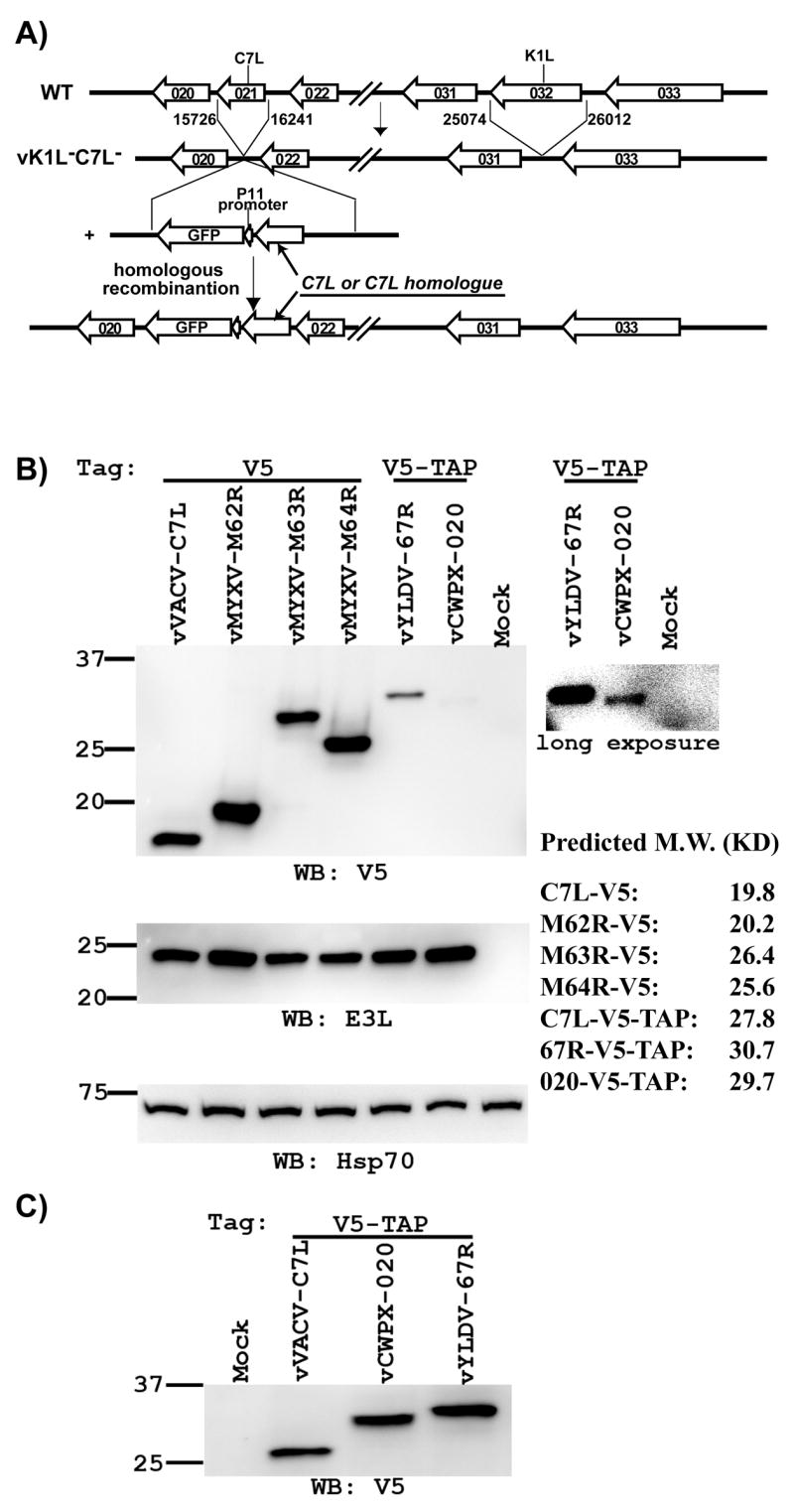
Construction of recombinant VACV with its K1L deleted and its C7L substituted with a C7L homologue. (A). Schematic illustration of the construction and genomic organization of the recombinant VACV. The construction of K1L and C7L deletion mutant vK1L−C7L− was described previously (15). Recombinant VACV encoding the C7L homologue were constructed by homologous recombination of vK1L−C7L− and a plasmid encoding the C7L homologue and the green fluorescence protein (GFP). P11 indicates the VACV promoter that normally regulates late expression of the gene encoding the 11K protein (WR F18R). (B & C). The recombinant VACV expresses the expected C7L homologue. VERO cells were infected at a MOI of 10 PFU (B) or 25 PFU (C) per cell with the indicated viruses, which are referred by the name of ORF present at the C7L locus. The C7L homologue is tagged at its C-terminus with either a V5 or V5-TAP tag. At 8 hpi, the level of C7L homologue in infected cells was determined by Western blot with a monoclonal antibody (mAb) against V5. A longer exposure of the blot was shown on the right to illustrate the weaker band. On the same blot, the levels of VACV early protein E3L and host cell protein Hsp70 were also determined with an anti-E3L polyclonal antiserum and an anti-Hsp70 mAb. Hsp70 serves as a control for gel loading, while E3L serves as an indicator of VACV early protein expression. The size of the molecular weight marker in kilodaltons is shown on the left. The predicted molecular weights of the tagged C7L-homologues are listed on the right.
