Figure 3.
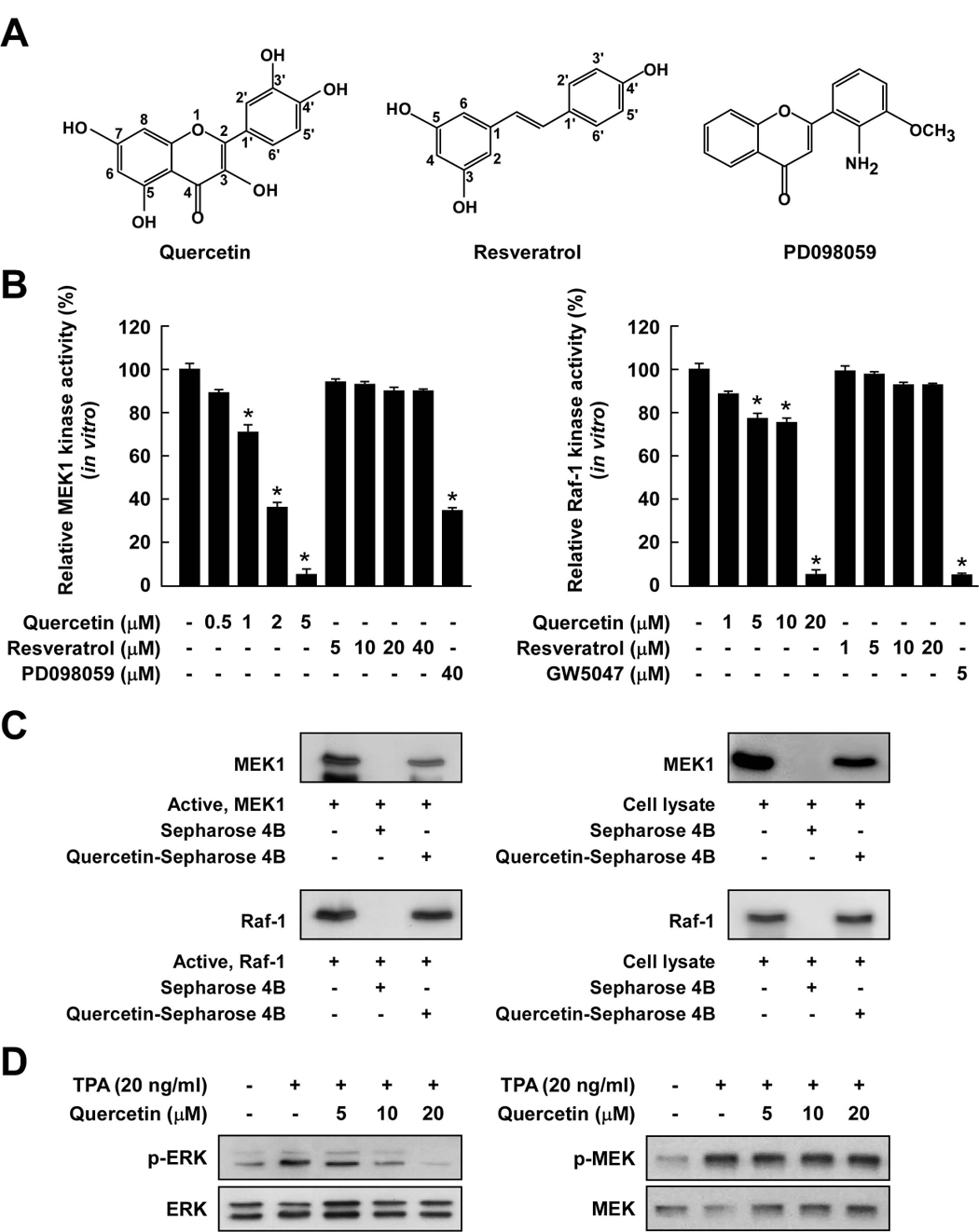
Comparison of the inhibitory effects of quercetin or resveratrol against activation of Raf/MEK/ERK signaling cascades. A, Chemical structures of quercetin, resveratrol, and PD098059. B, Quercetin inhibited MEK1 activity more strongly than Raf1 activity, whereas resveratrol did not inhibit either kinase activity. An in vitro MEK1 (left panel) or Raf1 (right panel) kinase assay was performed as described in the Materials and Methods, and the kinase activity is expressed as the percent inhibition relative to the activity of untreated MEK1 or Raf1 control. The asterisk (*) indicates a significant decrease (p < 0.05) in kinase activity between the groups treated with active MEK1 or Raf1 and quercetin (or resveratrol or PD098059 or GW5074) together and the group treated with active MEK1 or Raf1 alone. C, Quercetin specifically binds with either MEK1 or Raf1. The in vitro MEK1 (or Raf1)–quercetin binding was confirmed by immunoblotting using an antibody against MEK1 (left-upper panel) or Raf1 (left-lower panel): lane 1 (input control), MEK1 or Raf1 protein standard; lane 2 (control), Sepharose 4B was used to pull down MEK1 or Raf1; and lane 3, MEK1 or Raf1 was pulled down using quercetin-Sepharose 4B affinity beads. The ex vivo MEK1 (or Raf1)–quercetin binding was confirmed by immunoblotting using an antibody against MEK1 (right-upper panel) or Raf1 (right-lower panel): lane 1 (input control), whole-cell lysates from JB6 P+ cells; lane 2 (control), a lysate of JB6 P+ cells precipitated with Sepharose 4B beads; and lane 3, whole-cell lysates from JB6 P+ cells precipitated by quercetin-Sepharose 4B affinity beads. Each experiment was performed two times and representative blots are shown. D, Quercetin inhibited TPA-induced ERK phosphorylation but had no effect on MEK phosphorylation in JB6 P+ cells. JB6 P+ cells were treated with quercetin at the indicated concentrations (5, 10, or 20 µM) for 1 h before being stimulated by 20 ng/ml TPA for an additional 15 min. The cells were lysed and the levels of phosphorylated and total ERK and MEK proteins were determined by Western blot analysis as described in the Materials and Methods using specific antibodies against the respective phosphorylated and total proteins. Data are representative of three independent experiments that gave similar results.
