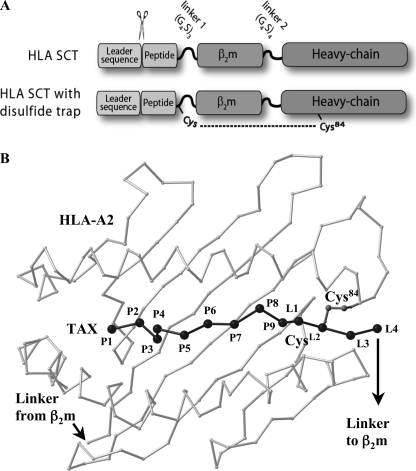
FIGURE 1.
HLA-I SCT format and positioning of the disulfide trap. A, schematic of SCT format and cysteine positions for HLA-I dtSCTs. HLA-I SCTs were expressed in mammalian cells using the SCT format originally described by Yu et al. (10) for murine MHC-I. The signal peptide is precisely cleaved within the endoplasmic reticulum to reveal the antigenic sequence that folds into the HLA-I peptide binding groove. Flexible linkers fuse the subunits of the heterotrimer for presentation of a pre-processed CD8 T cell epitope from a single open-reading frame. The first SCT linker perturbs conserved MHC interactions that normally engage the peptide carboxyl group; however, this decrease in C-terminal anchoring was offset by the introduction of a disulfide bond, which locks the peptide securely into the HLA-I groove. B, model of a disulfide trap A2/TAX SCT. Presented is a Cα trace of the peptide binding platform of HLA-A2 (light gray) as well as the TAX peptide (black) in the conformation observed in complex with the A6 T cell receptor (56). The first four linker residue Cα positions (L1–L4), as well as the Cys side chains that form a disulfide bond between linker position 2 (CysL2) and Cys84 were taken from the superimposed crystal structure of the dtSCT of Kb/OVA (24).