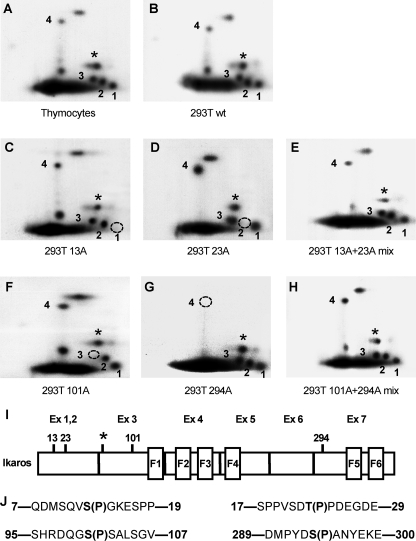
FIGURE 1.
Identification of novel Ikaros phosphorylation sites. Two-dimensional phosphopeptide maps were generated with wild-type Ikaros from murine thymocytes (A) and with wild-type and mutant Ikaros proteins expressed in HEK293T cells (B–H). Phosphopeptides representing novel phosphorylation sites are numbered 1–4. A star indicates a phosphopeptide representing a previously identified phosphorylation site (amino acid 63). Phosphomimetic Ikaros mutants contain substitutions with alanine (A) or aspartate (D) at the indicated amino acids. Phosphopeptides that are absent in each mutant protein are indicated by a dashed circle. Simultaneous loading of 13A and 23A or 101A and 294A restores all phosphopeptides. I, positions of novel and previously identified (*) phosphorylation sites within the Ikaros protein. J, sequences surrounding novel Ikaros phosphorylation sites.