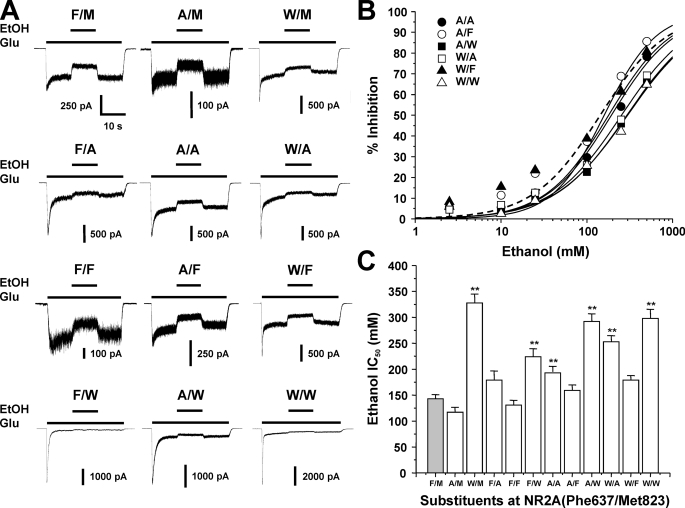
FIGURE 3.
Mutations at NR2A(Phe-637/Met-823) can alter NMDA receptor ethanol sensitivity. A, records are currents activated by 10 μm glutamate and 50 μm glycine and their inhibition by 100 mm ethanol (EtOH) in cells expressing NR1 and wild type NR2A subunits (F/M) or NR2A subunits containing various mutations at Phe-637 and Met-823. B, concentration-response curves for ethanol inhibition of glutamate-activated current in cells expressing various dual site substitution mutations at NR2A(Phe-637/Met-823). Data are means ± S.E. of 5–12 cells; error bars not visible were smaller than the size of the symbols. Curves shown are the best fits to the equation given under “Experimental Procedures.” The fit for the wild type NR2A subunit is shown as a dashed line. Plots for single-site mutations are not shown. C, average IC50 values for ethanol inhibition of glutamate-activated current in cells expressing NR1 and wild type NR2A subunits (F/M) or NR2A subunits containing various mutations at Phe-637 and Met-823. *, EC50 values that are significantly different from that for wild type NR1/NR2A subunits (**, p < 0.01; ANOVA followed by Dunnett's test). Results are means ± S.E. of 5–12 cells. Values for wild type, NR2A(F637A), and NR2A(F637W) are from Ref. 24; values for NR2A(M823A), NR2A(M823F), and NR2A(M823W) are from Ref. 22.