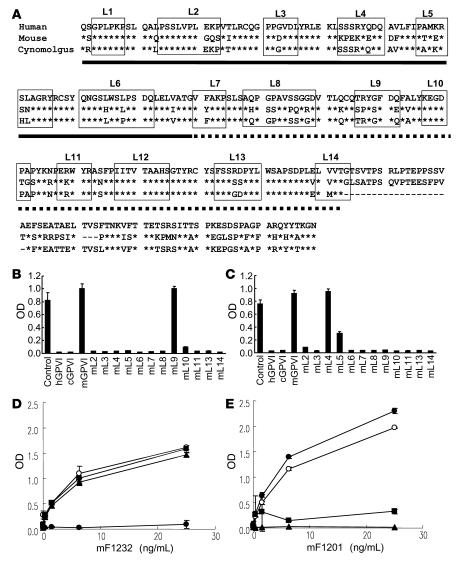
Figure 3. Binding of mF1232 and mF1201 to WT GPVI and to hGPVI mutants.
(A) Amino acid alignment of the extracellular domains of GPVI from 3 species are shown. Conserved amino acids among the 3 species are indicated by stars. The Ig-D1 and -D2 regions of GPVI are underlined with solid lines and dotted lines, respectively. To construct of the extracellular portion of GPVI, a comparative molecular modeling was carried out with “Homology” (Accelrys Software Inc.) using PDB 1UGN_A and PDB 1P6F_A as a template. The regions boxed with solid lines were defined as the loop structures. The abbreviation over the box denotes each loop number. (B and C) Fifty ng/ml of peroxidase-labeled mF1232 (B) or mF1201 (C) was incubated in an hGPVI-Fc–coated immunoplate for 60 minutes at 37°C with 1 μg/ml each of the absorption antigens hGPVI, mGPVI, cGPVI, or human/mouse chimera GPVI mutants. Human/mouse chimera GPVI mutant protein is represented as “mL plus number” meaning that the amino acid sequence of loop number on hGPVI is substituted for the counter loop region of mGPVI. (D and E) Peroxidase-labeled mF1232 (D) or mF1201 (E) were incubated with hGPVI-Fc– (open circles), mL9- (filled circles), mL4- (triangles), or mL5-coated (squares) plates. After incubation, the bound peroxidase-labeled mAb was measured. Data are presented as mean ± SD of triplicate determinations.