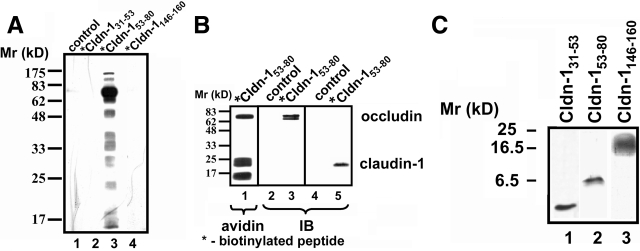
Figure 4.
Crosslinking of Cldn-153–80 to claudin-1 and occludin. A: Cells were incubated in either control medium (lane 1) or for 24 hours in the presence of biotinylated bait peptides at 200 μmol/L (*Cldn-131–53 [lane 2], *Cldn-153–80 [lane 3], or *Cldn-1146–160 [lane 4]). The cells were then washed, UV-crosslinked, harvested, and homogenized by nitrogen cavitation. Biotinylated bait peptide-protein conjugates were isolated by avidin affinity chromatography, resolved by SDS-PAGE, transferred to nitrocellulose, and detected with HRP-streptavidin. Only cells incubated with *Cldn-153–80 showed significant proteins crosslinked to the biotinylated peptide (lane 3). B: Cells treated with *Cldn-153–80 as described above were further subjected to boiling in 1% SDS before avidin affinity chromatography and streptavidin or immunoblot. Samples probed with HRP-streptavidin showed three prominent bands at ∼68 kDa, 23 kDa, and 17 kDa (lane 1). By immunoblot, the 68-kDa band was found to correspond to occludin (lane 3) and the 23-kDa band corresponded to claudin-1 (lane 5). Neither protein was isolated from control incubated cells (lanes 2 and 4). C: Cldn-131–53 (lane 1), Cldn-153–80 (lane 2), or Cldn-1146–160 (lane 3) at 200 μmol/L in HBSS+ were incubated for 30 minutes at room temperature and then resolved using Tris-tricine gel electrophoresis. Peptides were visualized directly in the gel by silver staining. Note that Cldn-153–80 primarily formed dimers (lane 2), whereas Cldn-131–53 was monomeric (lane 1) and Cldn-1146–160 formed a higher order complex (lane 3).