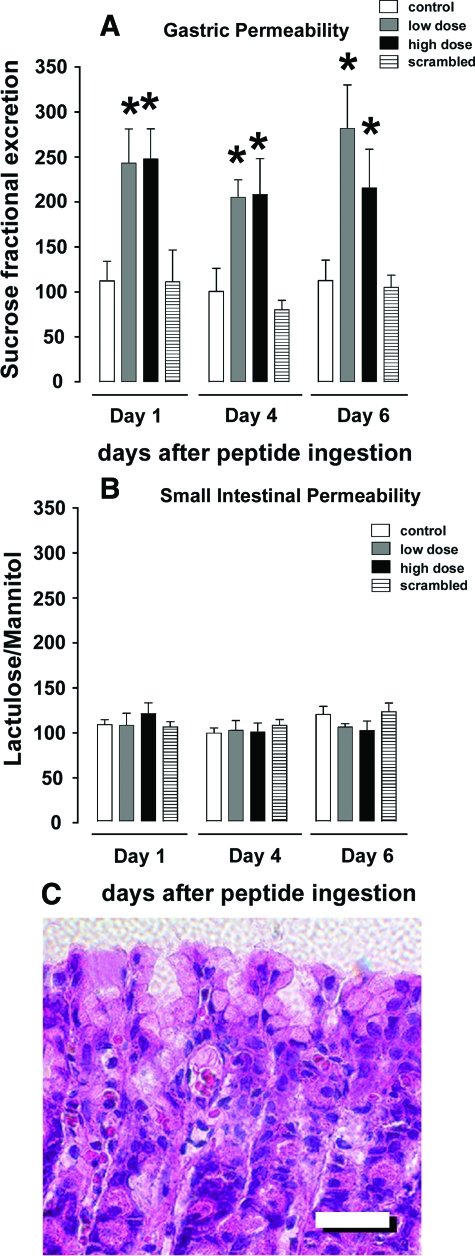
Figure 6.
Oral administration of Cldn-153–80 increased gastric permeability in vivo. A and B: Rats were administered sucrose, lactulose, and mannitol alone (control, white bars) or along with Cldn-153–80 at either 0.1 mg/kg body weight (low dose, gray bars), 1 mg/kg body weight (high dose, black bars), or with 1 mg/kg scrambled peptide (stippled bars) by oral gavage. Permeability of the stomach (A) and small intestine (B) were assessed by measuring urine disaccharide content as described in Methods. Cldn-153–80 induced a significant increase in gastric permeability at both low and high dose (*, P < 0.05). C: H&E-stained section of gastric tissue from rats treated with high dose Cldn-153–80. Peptide administration did not induce any epithelial loss or altered mucosal architecture. Scale bar =100 μm.