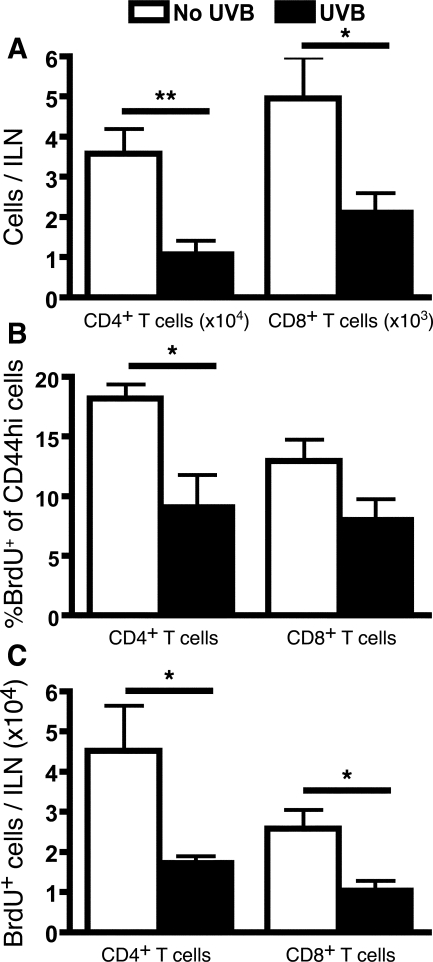
Figure 1.
UVB inhibits the increase in ILN effector T-cell number and proliferation in sensitized mice 9 days after sensitization. Mice were either unirradiated or irradiated with three daily doses of 90 mJ/cm2 UVB on the dorsum. Mice were sensitized on the abdomen with Ox, and 7 days later ears were challenged with Ox. The ILNs were examined 9 days after sensitization (48 hours after challenge). A: The increase in the number of ILN effector T cells attributable to sensitization was determined by subtracting the background number of effector T cells in unsensitized, but Ox ear-challenged mice. B: Mice were given BrdU in their drinking water from the time of sensitization. The increase in the proportion of CD44hi T cells expressing BrdU was determined by subtracting basal proliferation levels in unsensitized mice from that in sensitized mice. C: The number of BrdU+CD44hi T cells in sensitized mice after subtraction of basal proliferation numbers in unsensitized mice. n = 9 mice pooled from three individual experiments, means + SEM are shown. **P < 0.01 and *P < 0.05, comparing no UVB with UVB groups.