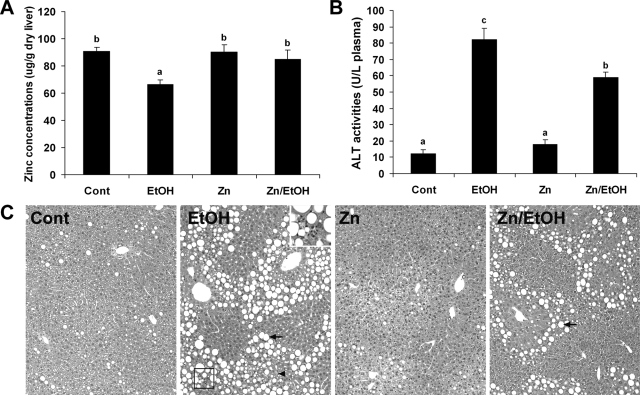
Figure 1.
Effect of zinc supplementation on hepatic zinc concentrations and liver injury in 129S6 mice chronically fed ethanol for 6 months. A: Normalization by zinc supplementation of ethanol-induced zinc deficiency in the liver. Zinc concentrations in the liver were measured by inductively coupled argon plasma emission spectroscopy. B: Inhibition by zinc supplementation of ethanol-induced elevation of serum ALT activities. C: Attenuation by zinc supplementation of ethanol-induced histopathological changes. Arrows: lipid droplets. Arrowhead: necrosis. Framed area: leukocytes infiltration. Inset is higher magnification of the framed area. H&E staining. Original magnification, ×130; inset, ×280. Results in A and B are means ± SD (n = 6). Significant differences (P < 0.05) among a, b, and c are determined by ANOVA.