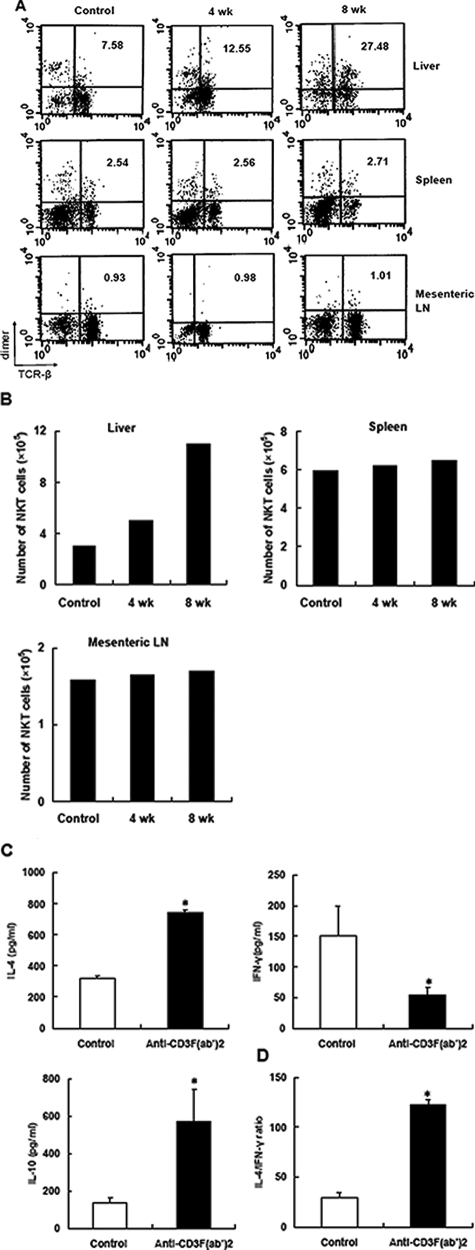
Figure 5.
Anti-CD3 administration expanded NKT cells and enhanced anti-inflammatory response. The proportion (A) and absolute number (B) of NKT cells in various lymphoid compartments of NOD mice after anti-CD3 treatment were determined by fluorescence-activated cell sorting analysis. Representative data of three experiments are shown. C: Hepatic NKT cells were isolated from control or anti-CD3 F(ab′)2-treated mice, respectively, and stimulated with anti-CD3 monoclonal antibodies (0.5 μg/ml) for 48 hours. The production of IL-4, IFN-γ, and IL-10 was determined in the supernatant by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. D: Splenocytes from antibody-treated or control mice 4 weeks after treatment were cultured in the presence of GAD500–585 at the concentration of 20 μg/ml for 48 hours, and then the supernatants were collected. The levels of IL-4 and IFN-γ were determined, and the ratio of IL-4 to IFN-γ is presented. Values are shown as means ± SD of four mice. *P < 0.05 as compared with control mice.