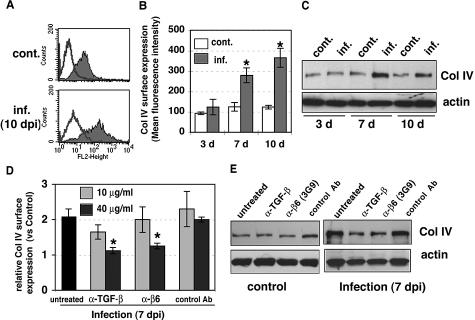
Figure 6.
Increased type IV collagen synthesis by CMV infection was blocked by anti-TGF-β and anti-αvβ6 neutralizing antibodies. A: Surface expression of type IV collagen was analyzed by flow cytometric analysis at 10 days after infection. Typical histograms from control (cont.) and infected (inf.) HUVECs are shown. Shaded areas represent expression of specific proteins. Lines represent isotype control. B: The results represent the mean fluorescence intensity of type IV collagen (mean ± SE) from three to seven experiments. Asterisks indicate surface expression in infected HUVECs as compared with uninfected controls (*P < 0.01). C: Cell lysates from control (cont.) or infected (inf.) HUVECs at 3, 7, and 10 days after infection were fractionated by 8% SDS-PAGE and blotted on nitrocellulose. Filters were incubated with anti-type IV collagen (Col IV) and anti-actin (loading control) antibodies. D: Surface expression of type IV collagen was analyzed by flow cytometric analysis at 7 days without antibody (untreated) or with anti-TGF-β neutralizing antibody (1D11), function-blocking anti-αvβ6 antibody (3G9), or mouse IgG1 isotype control antibody (control Ab). Relative surface expression as expressed by mean fluorescence intensity was normalized for control HUVECs in the same experiment. Results are the mean (±SE) from three experiments. Treatment with neutralizing antibodies significantly decreased surface expression of type IV collagen compared with infected cells (*P < 0.01). E: Effects of anti-TGF-β antibody and anti-αvβ6 antibody on type IV collagen production. Control and infected HUVECs were cultured without antibody (untreated) or with anti-TGF-β neutralizing antibody (1D11, 40 μg/ml), function-blocking anti-αvβ6 antibody (3G9, 40 μg/ml), or mouse IgG1 isotype control antibody (control Ab, 40 μg/ml) for 7 days. Lysates were fractionated by 8% SDS-PAGE and blotted. Filters were incubated with specific antibodies. Results are representative of at least four independent experiments.