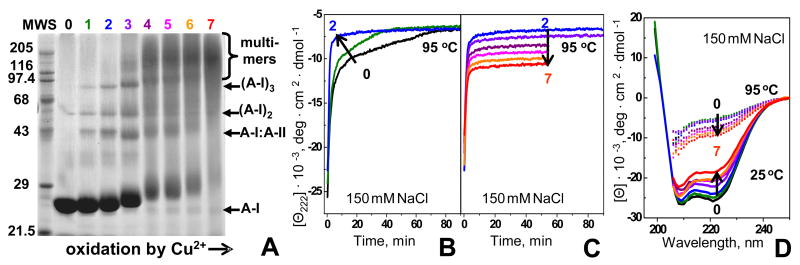
Figure 2.
HDL protein conformation and kinetic stability at various stages of oxidation by Cu2+. The data were recorded from solutions of HDL in buffer B (2.5 mg/mL protein (A) or 33 μg/mL protein, 150 mM NaCl (B–D)) that were oxidized by incubation with CuSO4 as described in Methods. Numbers correspond to oxidation stages in Fig. 1; 0 stands for nHDL.
(A) Protein cross-linking at various stages of HDL oxidation monitored by SDS PAGE. The gel was stained with Coomassie blue. A-II stands for S-S linked homodimer.
(B, C) Time course of HDL protein unfolding at various oxidation stages. HDL that were oxidized to stages 1–7 were subjected to a T-jump from 25–95 °C; protein unfolding was monitored by CD at 222 nm. Arrows indicate changes in the unfolding rates (B) or amplitudes (C) upon increase in the oxidation degree.
(D) Effect of HDL oxidation on the protein secondary structure before and after heat denaturation. HDL samples were oxidized to stages 1–7 and far-UV CD spectra were recorded at 25 °C. Next, the samples were incubated at 95 °C until CD changes were complete and the spectra were recorded again at 95 °C.