FIGURE 5.
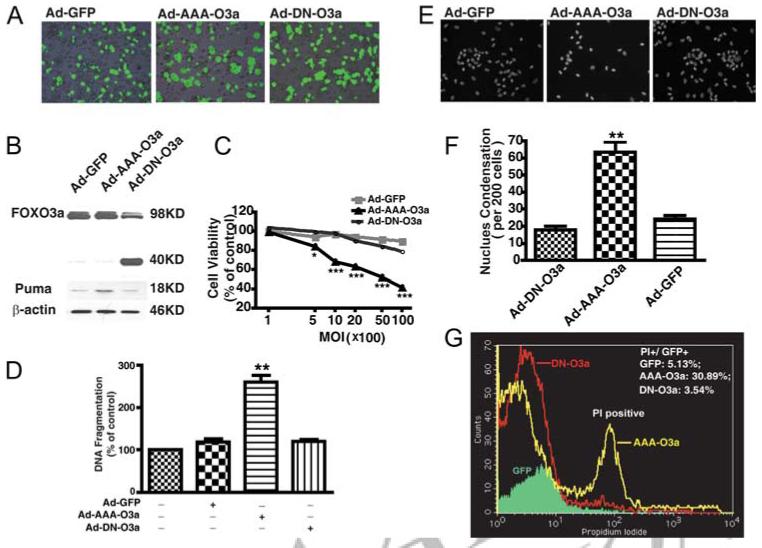
Overexpression of constitutively active FOXO3a induces macrophage cell death. A, Human MDM were infected with adenovirus vector containing a GFP reporter system. Infection efficiencies were monitored by taking fluorescence images 48 h after adenovirus infection. Ad-GFP is GFP control vector adenovirus; Ad-AAA-O3a is adenovirus expressing constitutively active FOXO3a; Ad-DN-FOXO3a is adenovirus expressing DN FOXO3a. B, After 72 h of adenoviral infection at 2000 MOI, FOXO3a overexpression was determined by immunoblotting for total FOXO3a. Constitutively active FOXO3a and endogenous FOXO3a both appeared at 98 kDa, while DN FOXO3a appeared at 40 kDa. In these samples, induction of Puma by FOXO3a overexpression was also determined by Western blotting. β-actin was used as a loading control. C, MDM were infected with various MOI of viral particles for Ad-GFP, Ad-AAA-O3a, and Ad-DN-FOXO3a. Seventy-two hours after infection, cell viability was determined by MTT assay; results shown were performed in triplicate and normalized as a percentage of GFP vector control. *, p < 0.05, ***, p < 0.001 compared with GFP vector control. D, At 2000 MOI of adenovirus, after 48 h of infection, apoptosis was determined by DNA fragmentation apoptosis ELISA. Results were representative of experiments performed in triplicate and normalized as percentage of control. **, p < 0.01 compared with GFP control vector. NS denotes no statistical difference from GFP control. E, Hoechst staining was performed to detect nuclear condensation after delivery of FOXO3a to MDM. F, Positive cells with nuclear condensation were counted every 200 cells per well with triplicate. **, p < 0.01 compared with GFP vector control. NS denotes no statistical difference from GFP control. G, After 72 h of adenoviral infection, human MDM were harvested and apoptosis was determined by PI staining and subsequent flow cytometry analysis. Numbers appearing in the upper right corner are percentage of PI-positive cells in GFP-positive cells. Results are representative of three independent experiments.
